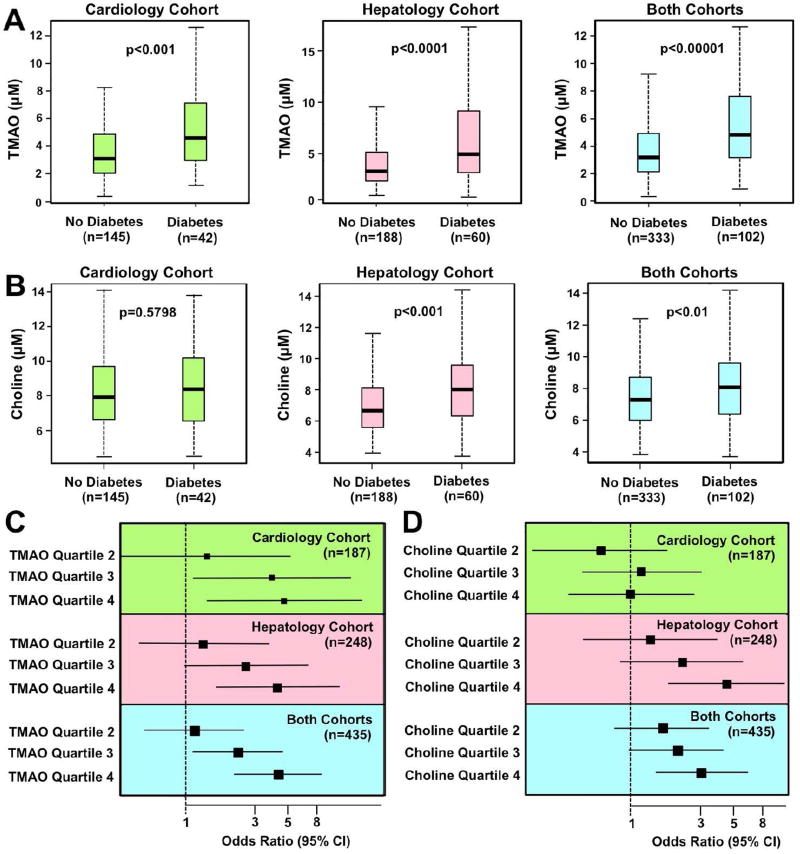
Figure 1. Elevated Circulating Levels of TMAO are Associated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Humans.
We recruited two separate cohorts of stable subjects in preventative cardiology (n=187) or hepatology clinics (n=248) to evaluate associations between fasting circulating choline or trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO) levels with prevalent type 2 diabetes (T2DM). The total number of subjects recruited in both studies was n=435. Patient demographics, laboratory values, and clinical characteristics are provided in Tables S1–S3 and Figure S1.
(A) Relationship of fasting plasma TMAO concentrations and prevalent T2DM. Boxes represent the 25th, 50th and 75th percentiles of plasma TMAO concentration, and whiskers represent the 10th and 90th percentiles.
(B) Relationship of fasting plasma choline concentrations and prevalent T2DM. Boxes represent the 25th, 50th and 75th percentiles of plasma choline concentration, and whiskers represent the 10th and 90th percentiles.
(C) Forest plots of the odds ratio of prevalent T2DM and quartiles of TMAO; bars represent 95% confidence intervals.
(D) Forest plots of the odds ratio of prevalent T2DM and quartile of choline; bars represent 95% confidence intervals.