Figure 1.
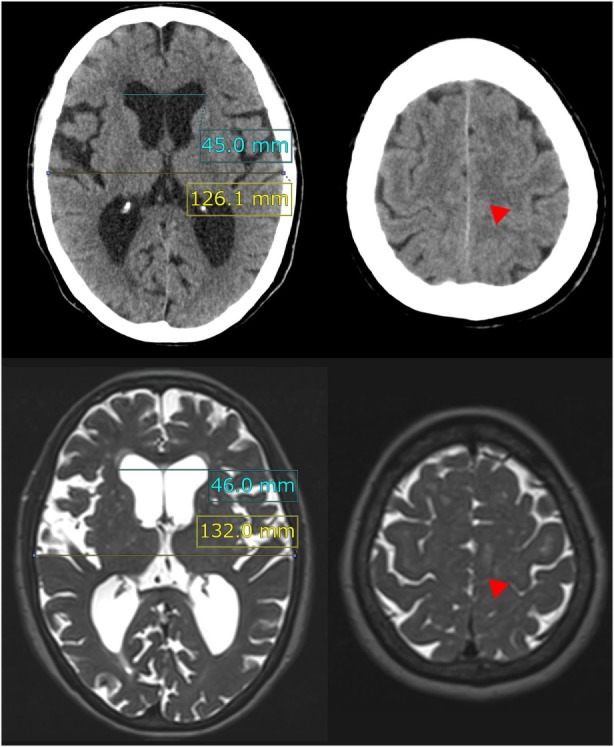
Evans index and high-convexity tightness. The upper figures show the traditional axial planes on CT scan and the lower figures show the T2-weighted MRI in a representative case of idiopathic NPH. The Evans index is measured as the maximal width of the frontal horns of the bilateral ventricles (sky blue line) to the maximal width of the internal diameter of the cranium (yellow line) on the basis of the axial planes on CT or MRI. In this case, the Evans index was calculated as 0.36 on CT scan and 0.35 on MRI. Red arrowheads indicate the high-convexity tightness which means decreased subarachnoid spaces at the convexity.
