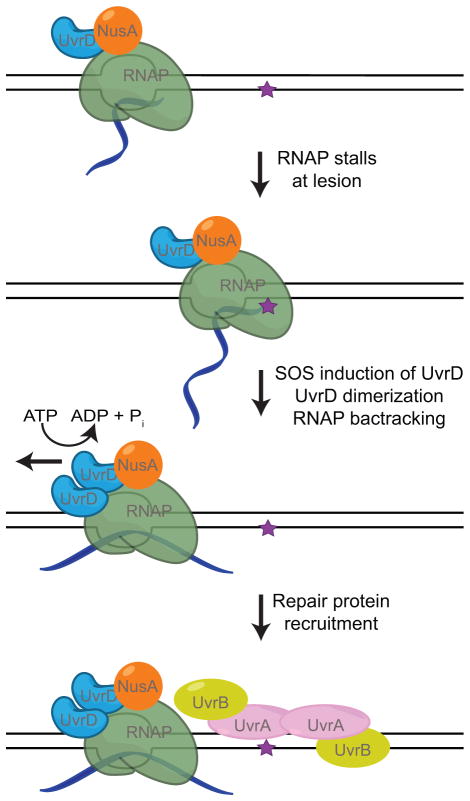
Figure 4. UvrD-dependent TCR.
UvrD and NusA associate with RNAP throughout transcription elongation. Upon induction of the DNA damage response the concentration of UvrD increases (113, 114) resulting in UvrD dimerization and activation of its helicase activity. With the help of NusA, UvrD pushes RNAP backwards without collapsing the transcription bubble possibly using its helicase activity to unwind the upstream edge of the bubble. As with the Mfd-dependent TCR pathway, UvrD-dependent TCR joins general NER at the damage verification step. However, transcription elongation can resume after UvrD-dependent TCR with the assistance of anti-backtracking factors.