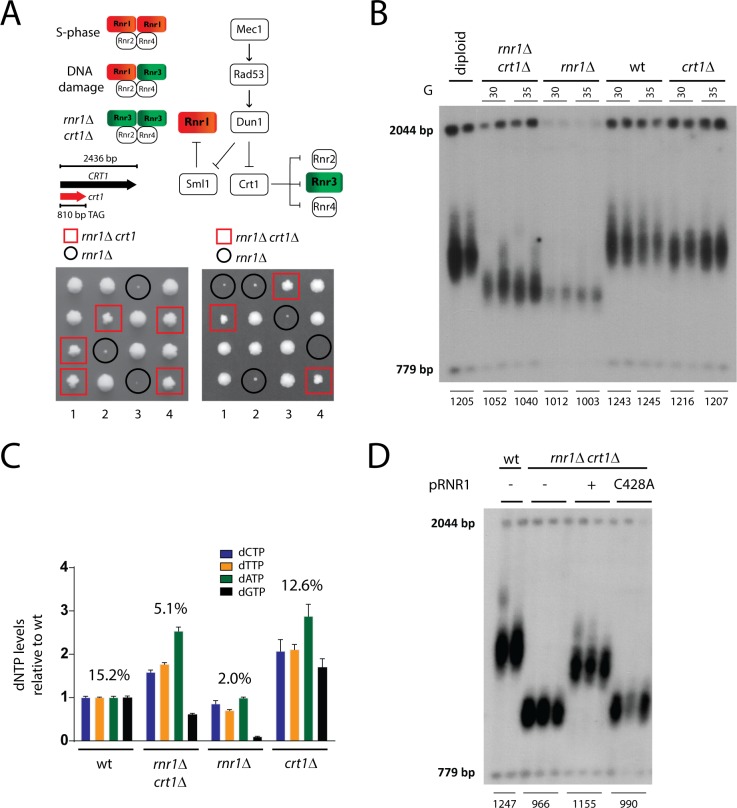
Fig 1. The loss of Rnr1 causes short telomeres that are stably maintained.
A) Mec1ATR regulates RNR activity and abundance via its downstream effector kinases Rad53 and Dun1. Dun1 phosphorylates Sml1 and releases its inhibitory effect on Rnr1 activity. Upon phosphorylation by Dun1, the repressive effect of Crt1 on Rnr2/3/4 transcription is abolished. The major RNR complex present in S-phase of the cell cycle consists of a tetramer containing two large Rnr1 subunits. Rnr3 is usually expressed at low levels but is upregulated in response to DNA damage. Sequencing of the CRT1 gene identified a premature stop codon that overcame the slow growth defect of rnr1Δ mutants, indicating that an RNR complex containing only Rnr3 as large subunits can compensate for the loss of Rnr1 in terms of cell viability. Tetrad analysis of spores derived from RNR1/rnr1Δ CRT1/crt1 (left) and RNR1/rnr1Δ CRT1/crt1Δ (right) heterozygous diploids indicate that the crt1 suppressor mutation behaves as a single Mendelian trait and phenocopies the full deletion of CRT1 in the suppression of impaired growth. For each heterozygous diploid four tetrads (1–4) have been analyzed by dissection. B) Telomere length analysis by Southern blotting. Following meiotic segregation heterozygous diploid RNR1/rnr1Δ CRT1/crt1Δ mutants have been dissected and the ability to maintain Y´ telomeres has been analyzed in the indicated spore colonies (2 biological replicates over 2 serial dilutions in liquid culture; approximately 30 and 35 generations after meiotic segregation). The telomere shortening of rnr1Δ crt1Δ double mutants resembles the one of rnr1Δ single mutants. C) dNTP pools and dGTP ratios (in %) were measured in the indicated strains. rnr1Δ mutants show lower dNTP levels and dGTP ratios when compared to wild type cells. CRT1 mutation results in an elevation of dNTP levels of rnr1Δ mutants but dGTP levels remain below wild type levels. Mean values +/-SEM are indicated. All values are shown as fold change over the individual dNTP levels of the wild type (set to 1). n(wild type) = 9; n(rnr1Δ crt1Δ) = 3; n(rnr1Δ) = 3; n(crt1Δ) = 2. D) Telomere length analysis by Southern blotting showing that rnr1Δ crt1Δ mutant telomeres are short but stably maintained. The plasmid-born expression of wild type Rnr1 for 200 generations restored telomere length of rnr1Δ crt1Δ mutants to a large extent. The expression of the catalytic inactive Rnr1-C428A did not affect telomere length in rnr1Δ mutants. Represented are biological replicates of the indicated strains.