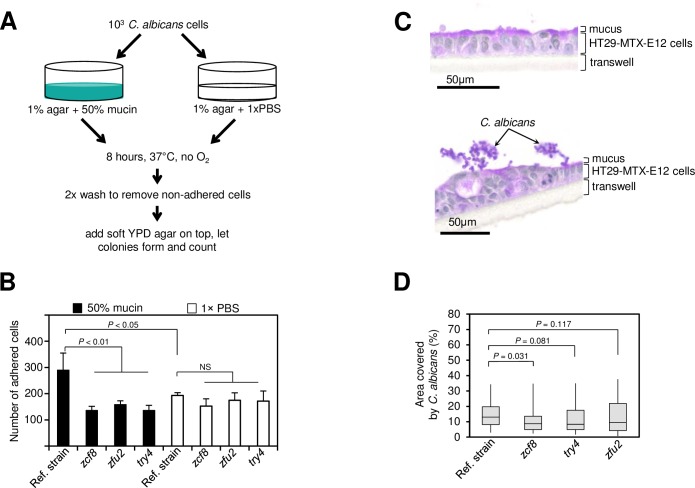
Fig 7. The regulators ZCF8, ZFU2 and TRY4 promote adherence.
(A) Schematic representation of in vitro assay to probe the ability of C. albicans cells to attach to a surface covered with intestinal mucin. (B) Plotted is the number of C. albicans cells (wild-type reference strain or deletion mutants) that remain attached to a semisolid surface containing either mucin (black bars) or PBS (white bars). Bars represent the mean ± S.D of at least three independent experiments; statistical analysis by t-test as described in Materials and methods. (C) C. albicans cells assemble in clusters on top of mucus-producing human intestinal epithelial cells HT29-MTX-E12. Shown are PAS-stained sections of HT29-MTX-E12 cells after 21 days of growth on transwells. Uninfected cells (top) and cells incubated with C. albicans (bottom). (D) Quantification of the attachment of C. albicans (wild-type reference strain or the indicated deletion mutants) to HT29-MTX-E12 cells grown on transwells. Plotted is the percentage area on top of the monolayer that was covered by fungal cells (as described in Materials and methods). Shown is the median (horizontal line in the middle of the box) with interquartile range (grey box) and the distance to the minimum and maximum values (whisker). Statistical analysis by the Mann-Whitney test. P values are indicated on top of each comparison.