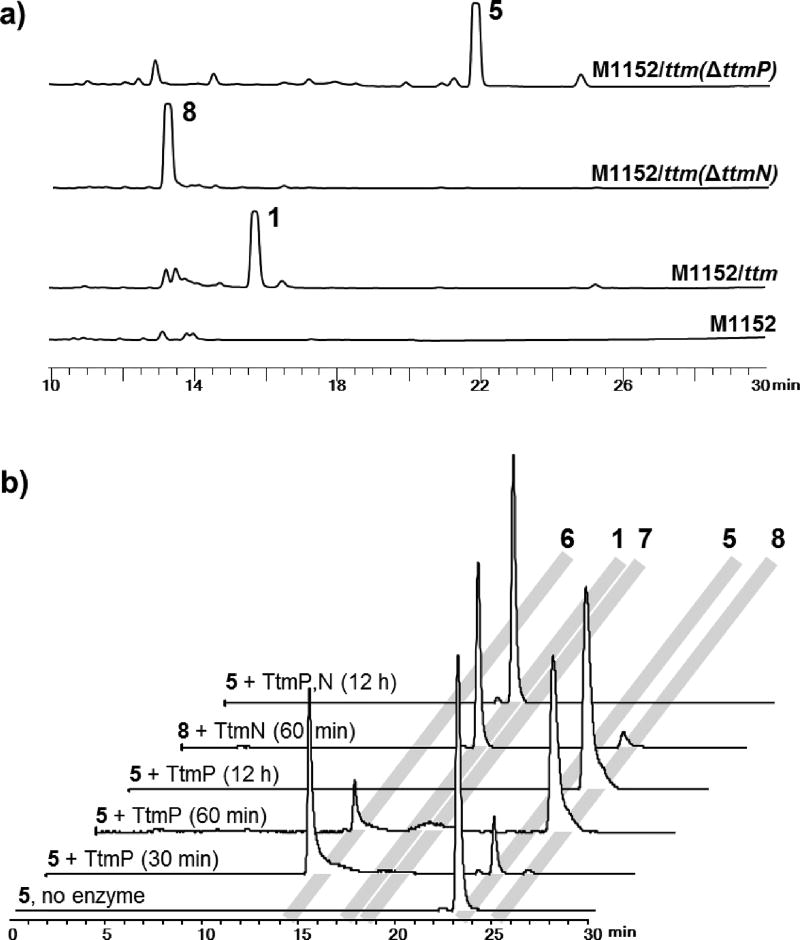
Figure 2.
In vivo and in vitro characterization of the C–H bond oxidation-amidation in the biosynthesis of thiotetroamide C. a) HPLC chromatograms (239 nm) of organic extracts of the heterologous host harboring ttm gene cluster, and ΔttmP and ΔttmN mutants. b) HR-LCMS analysis of the in vitro assays showing three sequential oxidation reactions catalyzed by the CYP450 TtmP to ultimately form the carboxylic acid product 8, which was further amidated by the Mg2+/ATP-dependent amidotransferase TtmN with l-glutamine as the preferred amino donor to generate the final amide product 1. All traces are extracted ion chromatograms (EICs) for m/z 268.1002, 239.1100, 255.1049, 253.0893, and 269.0842 that correspond to [M+H]+ of 1 and 5–8, respectively.