Figure 1.
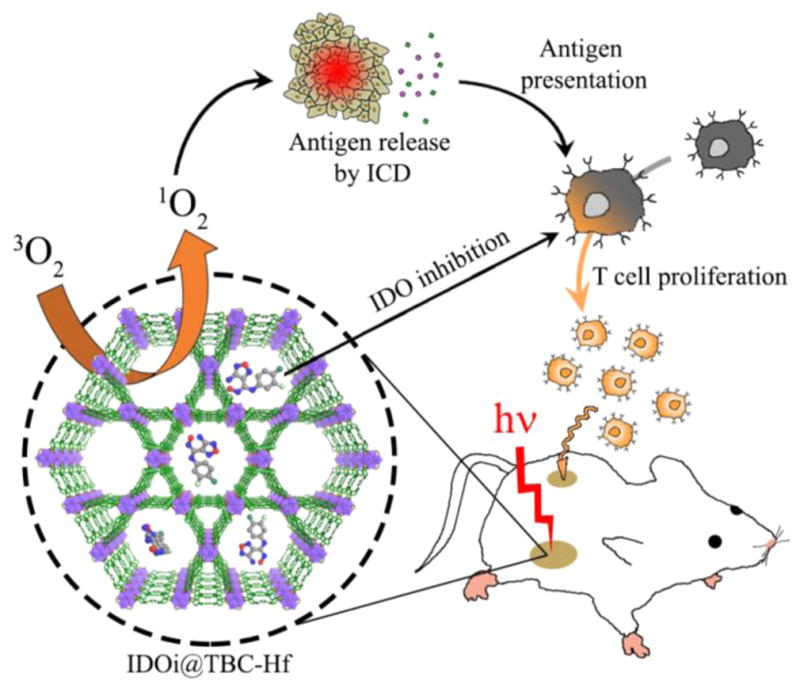
Schematic presentation of combined PDT and immunotherapy by IDOi@TBC-Hf. Local injection of IDOi@TBC-Hf and light irradiation generate reactive oxygen species, causing immunogenic cell death (ICD) and releasing tumor-associated antigens which are presented to T cells. Meanwhile, the IDO inhibitor released from IDOi@TBC-Hf modulates tryptophan/kynurenine catabolism to activate the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. The combination of antigen presentation from PDT and checkpoint blockade by IDO inhibition causes T cell proliferation and infiltration, leading to not only eradication of local, treated tumors but also rejection of distant, untreated tumors.
