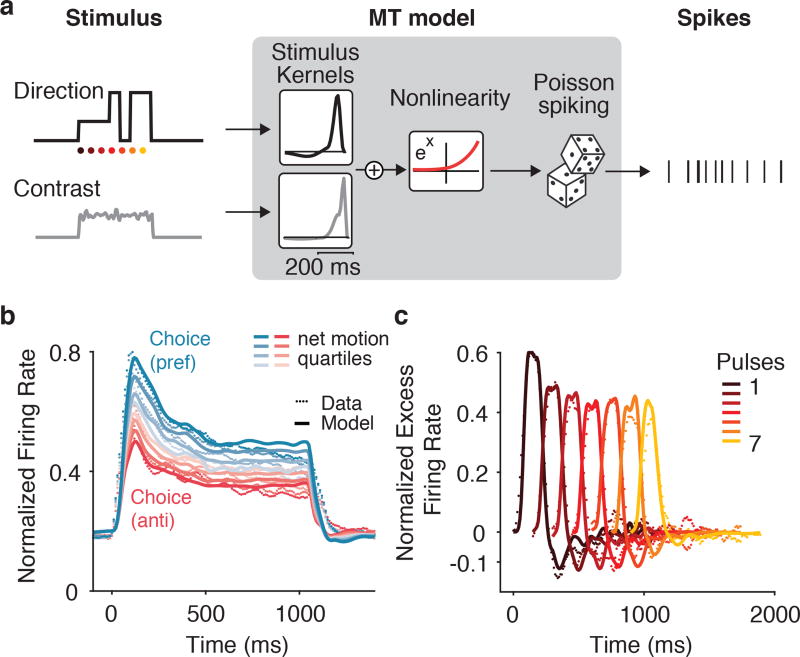
Figure 3.
MT temporal weighting explained by linear-nonlinear (LN) model. (a) Schematic of modeling approach. The contrast and direction of each Gabor are summed spatially and form two temporal inputs to a Generalized Linear Model (GLM). The recovered population average temporal filters for contrast and direction (insets in diagram) show brief integration of these inputs. The filtered output is then passed through an exponential nonlinearity to generate the rate of a conditionally –Poisson spiking process. (b) Population (n = 113) PSTH for MT (dotted lines) superimposed with model prediction (solid lines). (c) Population (n = 113) average PTA (dotted lines) superimposed with model PTA (solid lines).