Fig. 4.
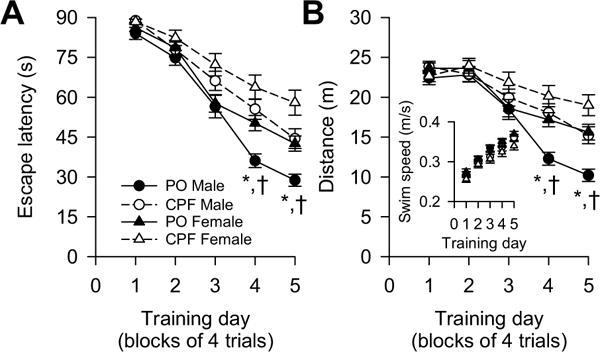
Effect of prenatal exposure to chlorpyrifos (CPF) on the acquisition phase of Morris water maze task. Graphs show (A) average escape latency and (B) average distance traveled by CPF- and peanut oil (PO)-exposed offspring per training day. Inset in B shows swim speed of male and female offspring prenatally exposed to CPF or PO. Data points and error bars represent mean and SEM, respectively, of results obtained from same groups of animals as in Fig. 1C. According to Tukey-Kramer post-hoc test for pairwise comparisons: *, p < 0.05 PO males vs. CPF males; †, p < 0.05 PO males vs. PO females.
