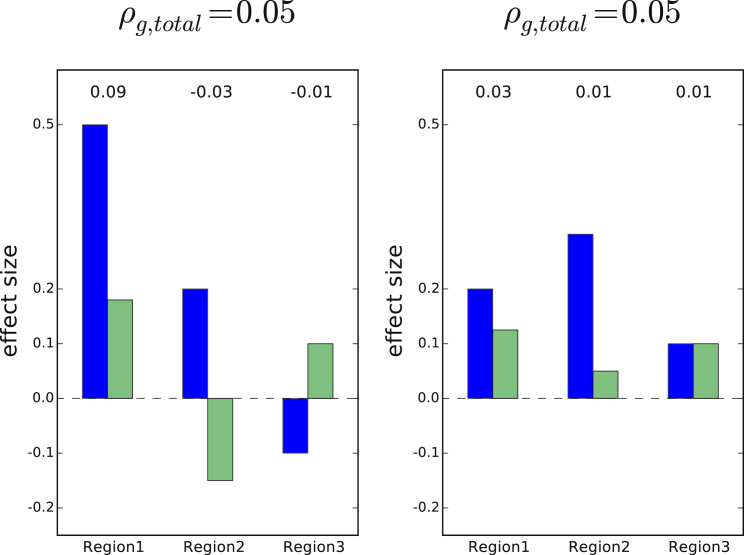
Figure 1.
Examples of Two Different Distributions of Local Genetic Covariances that Result in the Same Total Genetic Covariance
Covariances shown at the top of each bar; total genetic covariance ( = 0.05). In the left example, the total genetic covariance is a summation of a large positive local genetic covariance at region 1 and two smaller negative local genetic covariances at region 2 and region 3 (e.g., regions 2 and 3 impact traits through a different pathway than region 1). In the right example, the total genetic covariance is a summation of small positive local genetic covariances (e.g., all three regions impact both traits through the same pathway). Positive local genetic covariance can be interpreted as a locus driving a pathway that regulates two traits in the same direction, and negative local genetic covariance the opposite direction.