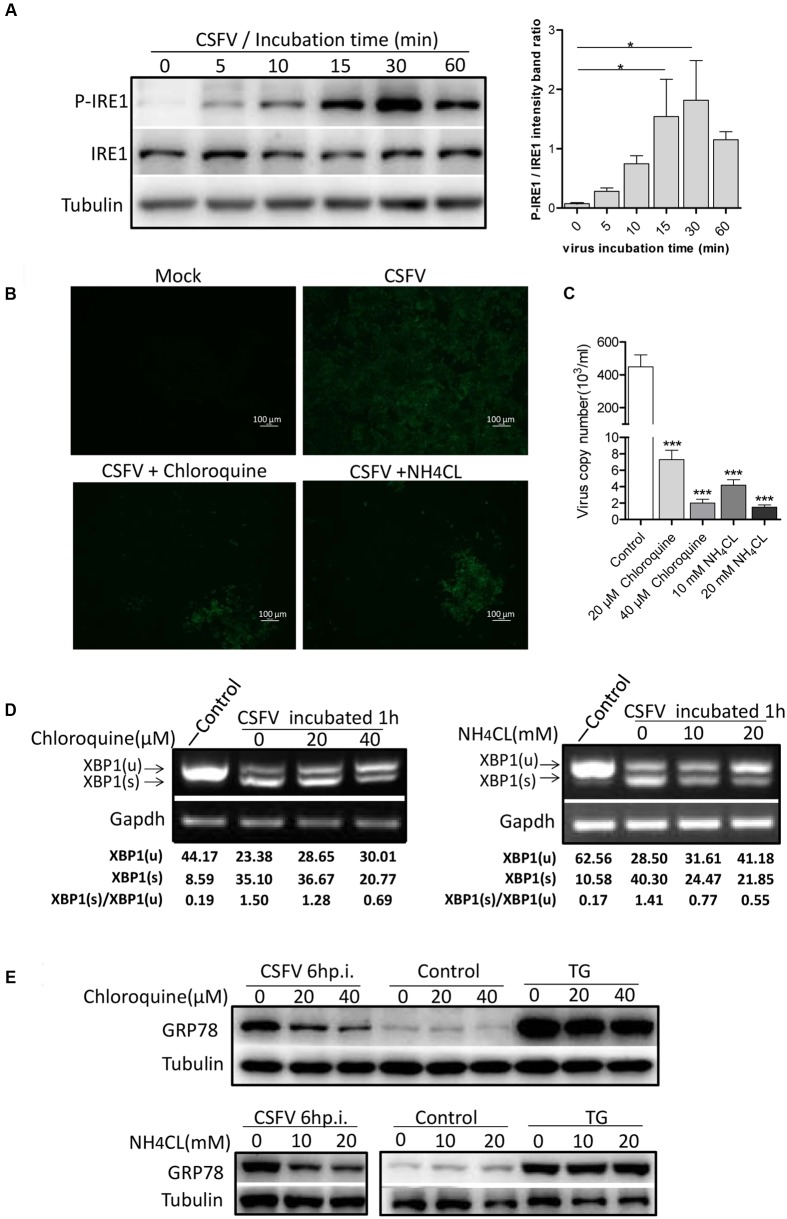
FIGURE 3.
Classical swine fever virus induces the activation of the IRE1 pathway during or soon after virion entry. (A) PK-15 cells incubated with CSFV for different time periods (0, 5, 10, 15, 30, and 60 min) at 37°C. Cell lysates were collected at the indicated time points and analyzed for the phosphorylation level of IRE1 by immunoblotting. Error bars represent the mean ± SD of 2 independent experiments; one-way ANOVA test; ∗P < 0.05. (B–E) PK-15 cells were pretreated with NH4CL (0, 10, and 20 mM) or Chloroquine (0, 20, and 40 nM) for 3 h, then incubated with CSFV (MOI = 1) combined with NH4CL or Chloroquine at corresponding concentrations for 1 h. The inhibitory effect of virus entry by NH4CL or Chloroquine were analyzed by the indirect immunofluorescence (B) and q-PCR (C). The cell RNA were collected after incubation, and cell lysates were collected after 6 h post infection. The splicing levels of XBP1 were analyzed by semi-quantitative PCR as described in Materials and Methods (D) and the expression of GRP78were analyzed by immunoblotting (E). Results of a representative experiment of 2 independent experiments are shown.