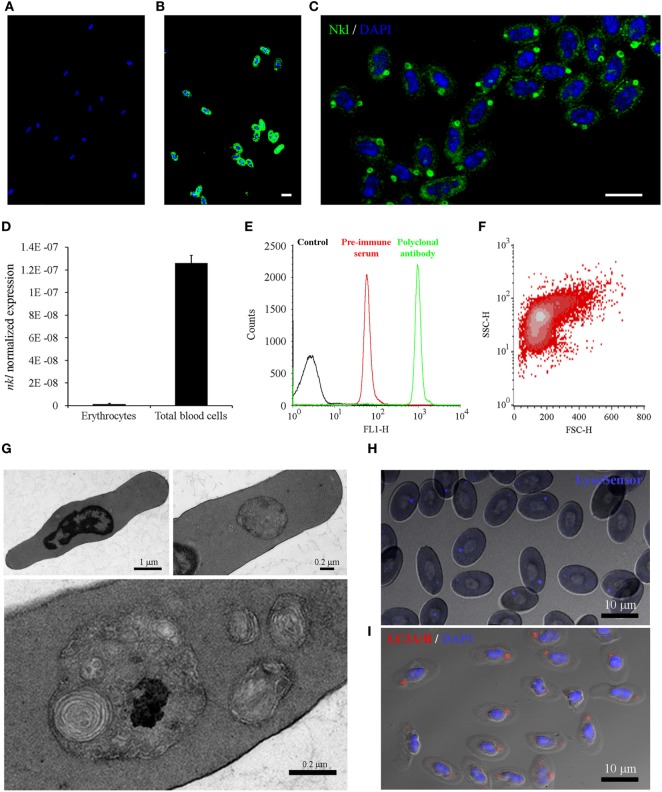
Figure 5.
Analysis of Nkl in erythrocytes by confocal microscopy, qPCR and flow cytometry, and the characterization of the cytoplasmic structures containing Nkl. (A,B) Immunocytofluorescence of purified erythrocytes stained with the rabbit preimmune serum (A) or the anti-Nkl polyclonal antibody (B), and the secondary antibody Alexa Fluor 488 goat anti-rabbit IgG. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Scale bar, 10 µm. The nonspecific fluorescence of the preimmune serum was not registered in samples stained with the polyclonal antibody. (C) Nkl was mainly detected in a large, spherical structure. Moreover, small puncta were also present in the cytoplasm. Scale bar, 10 µm. (D) Normalized expression of nkl in total blood cells and in purified erythrocytes. Bars represents the mean plus SD of 3 individual samples. (E) FL1-H fluorescence profile of purified erythrocytes stained with preimmune serum and polyclonal antibody. A specific signal of the antibody was clearly registered. (F) FSC/SSC density plot of FL1-H positive cells gated between 262-9910 log scale. (G) Description of the Nkl-positive vesicles by TEM. Almost all turbot erythrocytes present a large, double-membrane bound structure in the cytoplasm, although a few smaller ones are also observed (H) LysoSensor Blue staining of turbot erythrocytes. The spherical structures containing Nkl are LysoSensor-positive acidic vesicles. Scale bar, 10 µm. (I) Immunocytofluorescence of purified erythrocytes stained with the rabbit anti-LC3A/B polyclonal antibody, and the Alexa Fluor 546 goat anti-rabbit IgG as secondary antibody. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Scale bar, 10 µm. Nkl, Nk-lysin; qPCR, quantitative polymerase chain reaction; TEM, transmission electron microscopy.