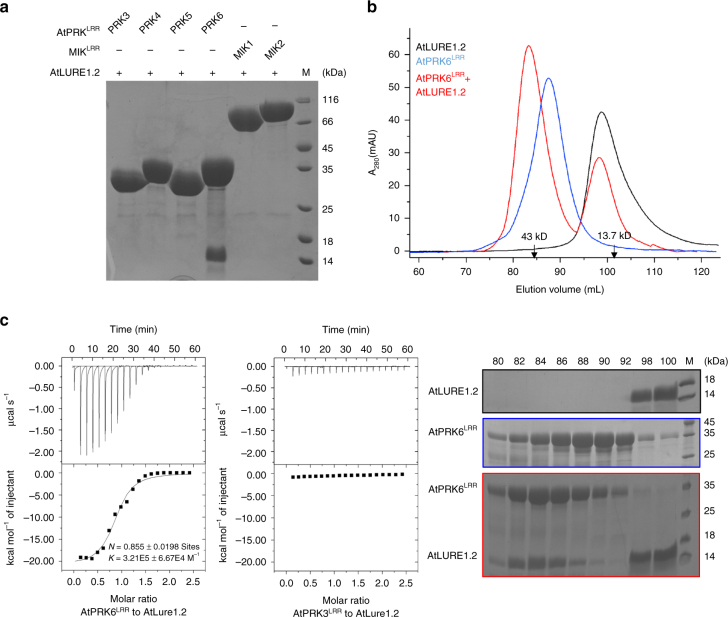
Fig. 1.
AtPRK6LRR specifically interacts with AtLURE1.2 in vitro. a AtLURE1.2 interacts with AtPRK6LRR in a pull-down assay. The purified AtPRKLRR and MIK1LRR, MIK2LRR proteins with 6 × His at the C-terminus bound to Ni-NTA were individually incubated with an excess of AtLURE1.2 protein. After extensive washing, the bound proteins were eluted and visualized by Coomassie blue staining following by SDS-PAGE. b AtLURE1.2 binding does not alter the monomeric state of AtPRK6LRR in solution. Upper panel: gel filtration profiles of AtPRK6LRR, AtLURE1.2, and AtPRK6LRR-AtLURE1.2 complex. The black arrows indicate the molecular weights around the AtPRK6LRR-AtLURE1.2 complex and AtLURE1.2. A280 (mAU), micro-ultraviolet absorbance at the wavelength of 280 nm. Lower panel: coomassie blue staining of the peak fractions shown on the top following SDS-PAGE. M, molecular weight ladder (kDa). Numbers on top of SDS-PAGE panel indicate elution volumes. c Measurement of the binding affinity between AtPRK6LRR and AtLURE1.2 by ITC. Left upper panel: twenty injections of AtLURE1.2 solution were titrated into AtPRK6LRR solution in the ITC cell. The area of each injection peak corresponds to the total heat released for that injection. Left lower panel: the binding isotherm for AtPRK6LRR-AtLURE1.2 interaction. The integrated heat is plotted against the molar ratio between AtLURE1.2 and AtPRK6LRR. Data fitting revealed a binding affinity of about 3.1 μM. Right panel: binding affinity between AtPRK3LRR and AtLURE1.2 by ITC