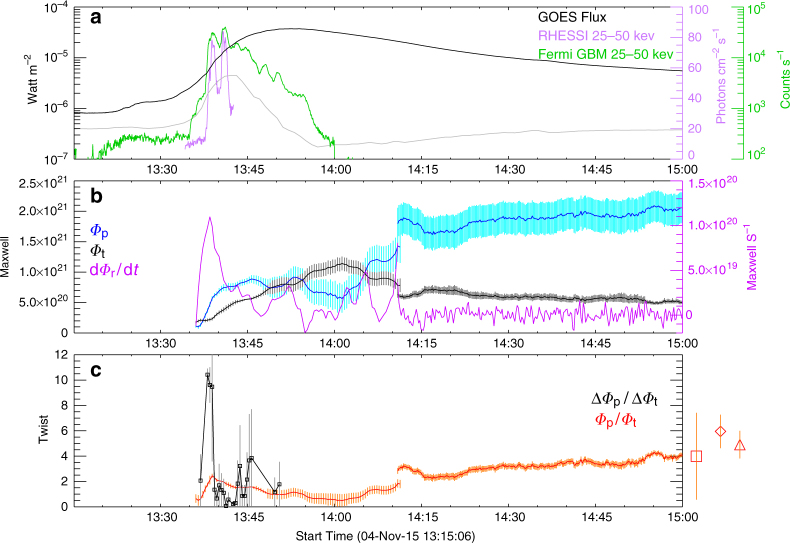
Fig. 6.
Temporal evolution of the poloidal and toroidal fluxes in the magnetic flux rope. a 0.1–0.8 nm soft X-ray flux observed by the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES), its time derivative in an arbitrary unit (gray), 25–50 keV hard X-ray (HXR) count rate observed by the Gamma-ray Burst Monitor (GBM) onboard the Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope, and 25–50 keV HXR photon flux observed by the Reuven Ramaty High-Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager (RHESSI). b Poloidal flux Φ p and toroidal flux Φ t of the magnetic flux rope. Also shown is the time derivative of reconnection flux Φ r = Φ p + Φ t. c Twist number of the magnetic flux rope as gauged by Φ p/Φ t and ΔΦ p/ΔΦ t. Marked on the right are Φ p/Φ t given by the Gold-Hoyle (square) and Lundquist (diamond) fittings and the Grad-Shafranov reconstruction (triangle; Methods section) of the interplanetary magnetic cloud, with the values and error bars given in Supplementary Table 1 (Methods section). Error bars of Φ p and Φ t are given by varying the detection threshold of the corresponding features (Methods section), and those of Φ r, Φ p/Φ t, and ΔΦ p/ΔΦ t are derived following the error propagation rules