Figure 4.
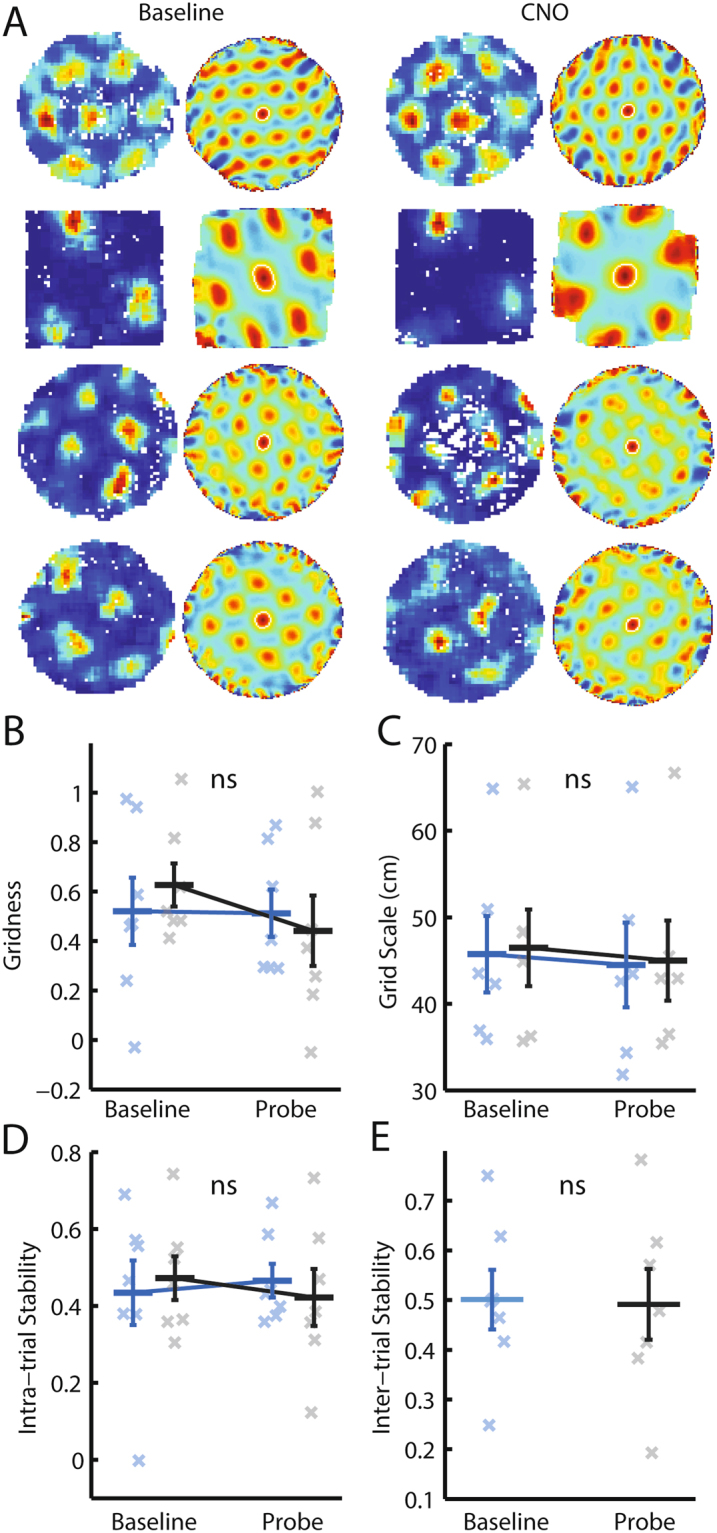
Modulating medial septal cholinergic activity has no effect on grid cell firing patterns. (A) Example ratemaps and spatial autocorrelograms from four grid cells (one in each row), in a baseline trial (left hand side) and a CNO probe trial (right hand side). (B–E) Blue = CNO, black = saline. Bars indicate mean ± SEM across all animals in each group. Crosses indicate average value for each animal in each group. Only cells with gridness > 0.3 in either a baseline or probe trial are included. (B–D) Stars indicate RM-ANOVA baseline vs probe * CNO vs saline interaction significance. ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05, ns = p > 0.05. (B) Degree of hexagonal regularity of grid cell firing patterns, as measured by the gridness score. (C) Grid cell scale in cm, measured as the median distance to the six peaks closest to the centre of the autocorrelogram. Only trials with gridness > 0.3 are included. (D) Intra-trial stability of grid cell firing patterns, as measured by the value at the centre of a cross-correlogram constructed from two ratemaps, one from each half of the trial. (E) Inter-trial stability of grid cell firing patterns, as measured by the value at the centre of a cross-correlogram constructed from two ratemaps, one from the baseline and one from the probe trial. No significant difference was found between the groups using a paired t-test.
