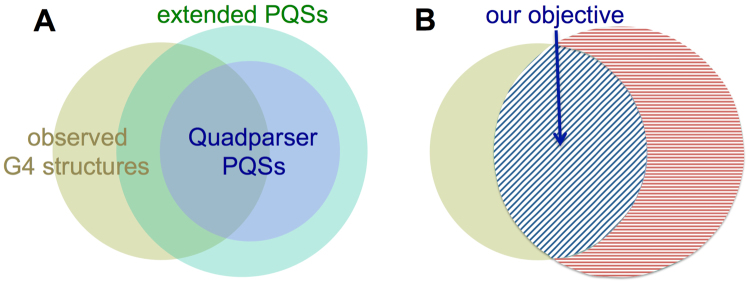
Figure 2.
Euler diagrams showing the overlap between the experimentally observed G4 structures (dark yellow disc) and the putative quadruplex sequences (PQSs) found via simple sequence motif search in the human genome. The violet disc in (A) represents the more conservative Quadparser (G3+N1−7G3+N1−7G3+N1−7G3+) sequences. The green disc in (A) represents the extended sequence motif with longer allowed maximum loop size - G3+N1−12G3+N1−12G3+N1−12G3+. Both motifs result in similarly high (46.37% and 50.96%) false positive rates, however, the extended motif covers a bigger portion of experimentally observed G4 structures (65.56% vs. 36.86%). (B) Represents the objective of our present work, which is to develop a machine learning model that, starting from the extended PQS motif definition, would correctly differentiate sequences that form stable G4 structures (blue-shaded overlap in (B)) from the ones that do not (red shaded part in (B)).