Figure 1.
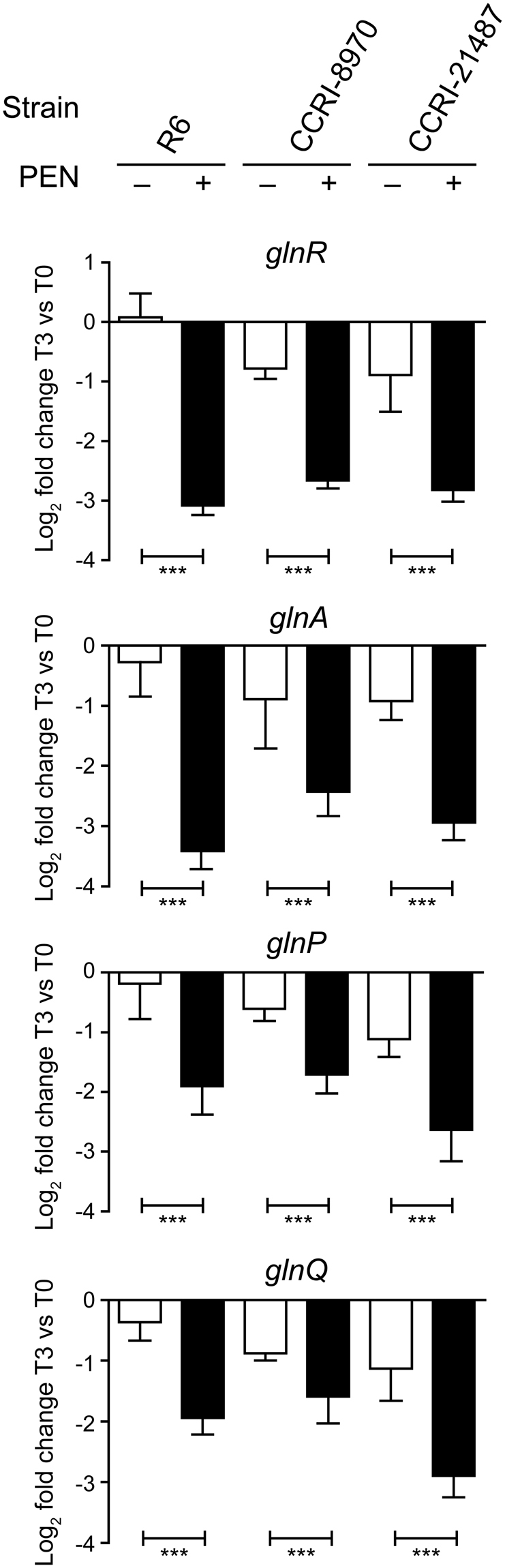
Validation of penicillin-induced alterations to glutamine metabolism gene expression in S. pneumoniae by qRT-PCR. Genes involved in glutamine metabolism (glnR, glnA, glnP and glnQ) found to be down-regulated after exposure to PEN by RNA-seq were validated by qRT-PCR. RNA levels were normalized based on the amplification signals of 16S ribosomal RNA. Graphs show the log2 fold change of expression at time T3 (corresponding to 40 min for R6, 28 min for CCRI-21487 and 85 min for CCRI-8970) over T0 in untreated (white bars) and PEN-treated (black bars) S. pneumoniae isolates. Results are displayed as mean ± SD of three biological replicates and significant differences are identified as determined by split plot design and Fisher’s F-test (***p ≤ 0.001).
