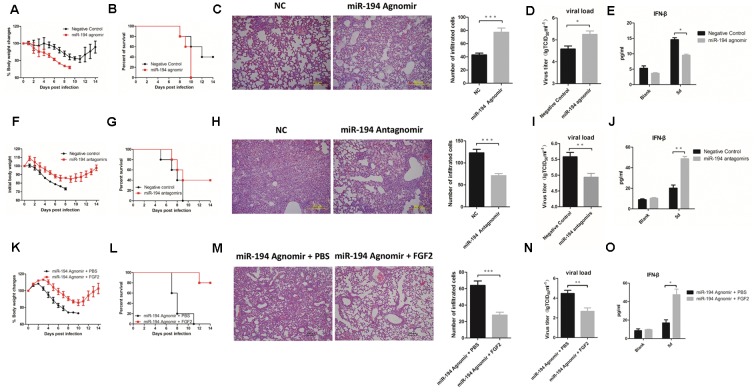
FIGURE 4.
miR-194 antagonism alleviates lung injury induced by IAV. WT B6 mice were sequentially inoculated intravenously with 4 nM miR-194 agomir or negative control per mouse 12 h prior to, as well as 1 and 3 days after allantoic fluid (AF) or virus (103 TCID50 of A/Beijing/501/2009) instillation. For miR-194 antagomir treatment, mice were sequentially inoculated intravenously with 8 nM miR-194 antagomir or negative control 12 h prior to, as well as 1 and 3 days after AF or virus (105 TCID50 of A/Beijing/501/2009) instillation. For FGF2 administration, WT B6 mice were inoculated intravenously with 4 nM miR-194 agonism plus 25 μg recombinant murine FGF2 protein per mouse 12 h prior to, as well as 1 day and 3 days after AF or virus (103 TCID50 of A/Beijing/501/2009) instillation. All of the data are shown as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM), and independent experiments were repeated three times. ∗P <0.05, ∗∗P <0.01, and ∗∗∗P <0.001. (A,F,K) Weight changes in treated B6 mice (n = 5). (B,G,L) Survival rates of treated B6 mice (n = 5). (C,H,M) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and quantification of lung tissues from treated mice at 5 days post-infection (dpi). (D,I,N) Virus titers of lung from treated mice (n = 6) determined based on the TCID50 assay at 5 dpi. (E,J,O) IFN-β cytokine levels in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluids (5 dpi) were determined by ELISA (n = 3).