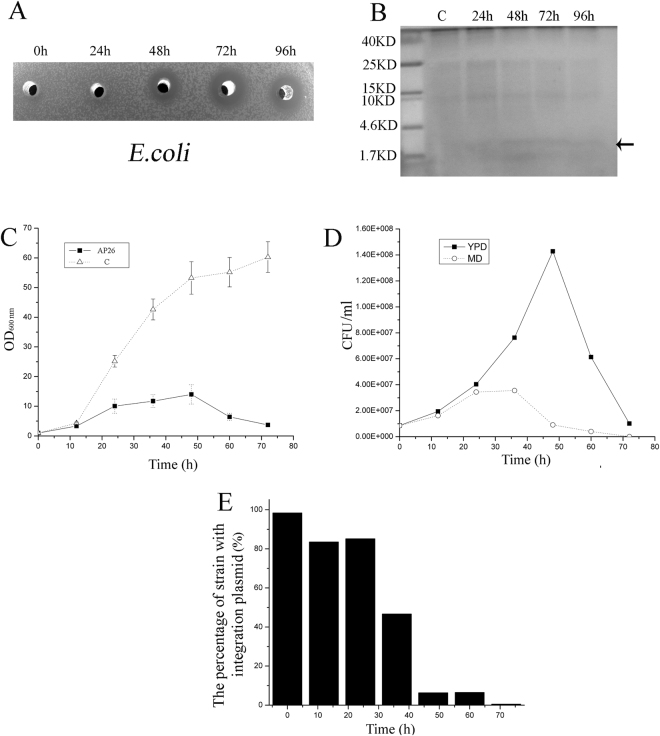
Figure 2.
The loss of the integration plasmid is a key factor affecting apidaecin expression. (A) Antimicrobial activity of fermentation supernatants (50-μl) sampled at different time points after induction (0, 24, 48, 72 and 96 h) against E.coli. (B) Tricine-SDS–PAGE analysis of apidaecin in fermentation supernatants. The left-hand lane was loaded with 10 μl of a protein molecular weight marker. Lane C: 10 μl of P. pastoris C strain 72 h fermentation supernatants. Lane 24 h–96 h: 10 ul of AP26 fermentation supernatants taken at 24 h, 48 h, 72 h and 96 h. (C) Strains AP26 and C were first grown in MD liquid medium at 30 °C for 48 h and then transferred into BMMY buffered methanol complex medium, with both cell concentrations at OD600 = 1 at the beginning. The growth curves were measured at 0, 24, 48 and 72 h respectively. (D) Following methanol induction, the CFU/ml of AP26 grown on MD and YPD medium were measured at 0, 24, 48 and 72 h respectively. (E) The percentage of integration plasmid loss of AP26 was calculated following methanol induction.