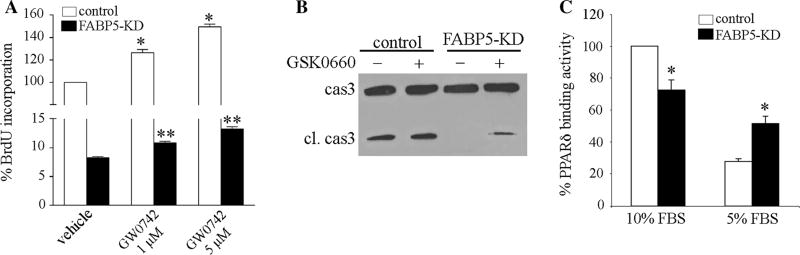
Fig. 6.
Role of PPARδ on FABP5-induced responses in ECs. a HUVECs were transduced with control shRNA or FABP5-shRNA. Cells were treated with DMSO or GW0742 at the indicated doses for 24 h. Cell proliferation was analyzed by BrdU incorporation using an ELISA kit. *p < 0.05 versus control/vehicle; **p < 0.05 versus FABP5-KD/vehicle. b FABP5-KD and control HUVECs were cultured in 5 % FBS-containing medium with or without PPARδ specific inhibitor GSK0660 (100 nM) for 24 h. Cells were harvested, and immunoblotting for caspase 3 was performed. c FABP5-KD and control HUVECs were cultured in 10 or 5 % FBS-containing medium for 24 h. DNA-binding activity of PPARδ in nuclear extracts was measured using an ELISA kit. *p < 0.05 versus control