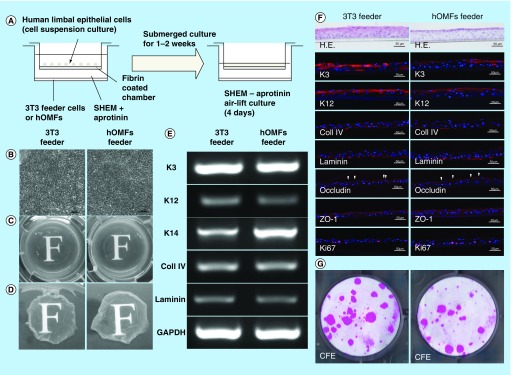
Figure 6. . Cultivation of human limbal epithelial sheets with two types of feeder cells.
(A) Illustrated cultivation methods of human limbal epithelial sheets. (B) Phase-contrast micrographs of epithelial sheets with 3T3 (left panel) and hOMF (right panel) feeder cells. Scale bars: 50 μm. (C) Photographs of both types of human limbal epithelial sheets. (D) Macroscopic view of both types of human limbal epithelial sheets after removing culture inserts. (E) Comparison of both types of human limbal epithelial sheet phenotypes by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. GAPDH was used as an internal control. (F) Histochemical comparison of the phenotypes of both types of human limbal epithelial sheets. Arrowheads indicate occludin expression. Scale bars: 50 μm. (G) Comparison of CFE in each sheet. Colonies were stained with rhodamine B after 2 weeks.
CFE: Colony-forming efficiency; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydogenase; H.E.: Hematoxylin & eosin; hOMF: Human oral mucosa middle interstitial tissue fibroblast; SHEM: Supplemental hormonal epithelial medium.