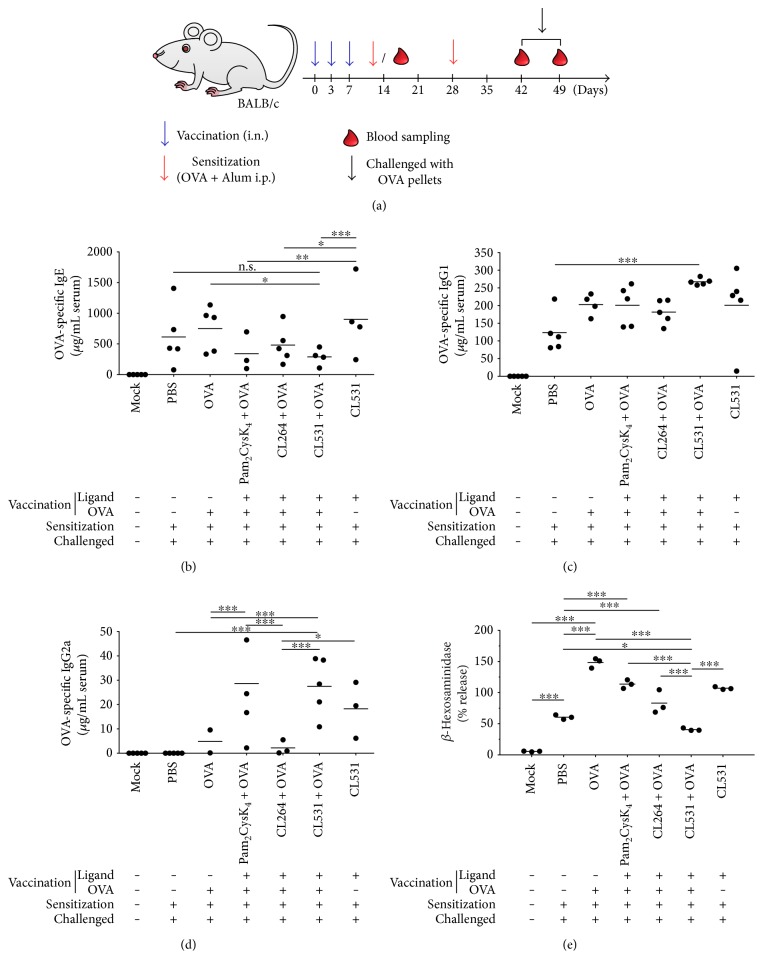
Figure 5.
Prophylactic vaccination with CL531 plus OVA suppresses OVA-specific IgE production while inducing OVA-specific IgG production in a mouse model of OVA-induced intestinal allergy. Schematic representation of prophylactic vaccination approach (a). Blue arrows represent intranasal (i.n.) vaccination or mock vaccination (in “Mock” group); red arrows represent intraperitoneal (i.p.) sensitization with 10 μg OVA with 2 mg Alum in 200 μL sterile PBS (or, in “Mock” group, with sterile PBS alone). Blood drops represent blood sampling from the tail after vaccination and sensitization or cardiac puncture after challenged with OVA-containing food pellets. Serum concentration of OVA-specific IgE (b), IgG2a (c), and IgG1 antibodies (d) was measured throughout the vaccination experiment by ELISA. β-Hexosaminidase release from RBL 2H3 cells upon crosslinking with OVA was performed with pooled sera from the final bleeding (e). Results are means ± SD from five mice per group (b, c, d) or means of three technical replicates measured using the same serum pool to sensitize the RBL 2H3 cells (e). ∗P < 0.05; ∗∗P < 0.01; ∗∗∗P < 0.001.