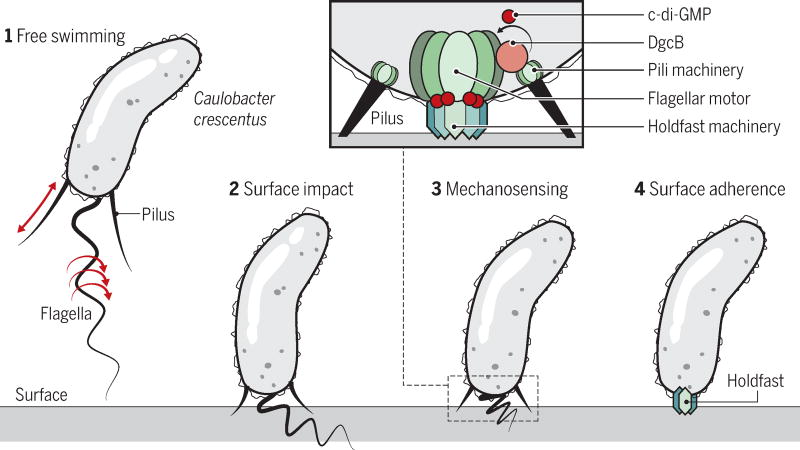
Figure 2. Surface sensing and attachment by Caulobacter crescentus.
When a free-swimming Caulobacter bacterium encounters a surface, either the intact flagellar motor, acting as a mechanosensitive channel, or a pilus, inhibited from retraction upon surface contact, stimulates localized c-di-GMP production that results in holdfast production and surface adherence. For the flagellum, the DgcB protein is responsible for c-di-GMP production at the cell pole, which binds to the HfsJ component of the holdfast synthesis machinery.