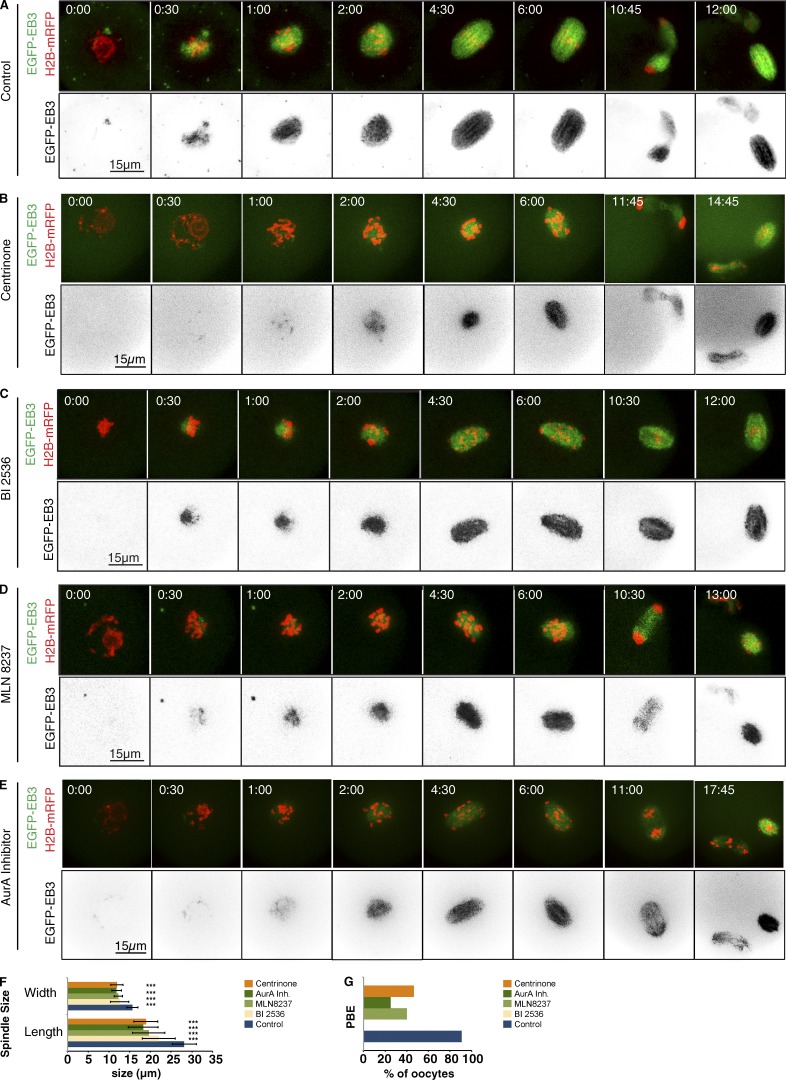
Figure 2.
Aurora A, Plk4, or Plk1 inhibition differently affect meiosis I progression. Time-lapse series of mouse oocytes expressing EGFP-EB3 (green, top; gray, bottom) and histone H2B-mRFP (red, top). Depicted are controls (A), oocytes treated with 2 µM centrinone (B), oocytes under Plk1 inhibition by treatment with 100 nM of the Plk1 inhibitor BI2536 (C), and oocytes treated with 1 µM Aurora A inhibitor 1 (AurA Inh 1) and 500 nM MLN8237 (E). Time in hours:minutes relative to NEBD. (A–E) Representative still images from NEBD until establishment of spindle bipolarity, anaphase I onset, and polar body extrusion under the different experimental conditions. After Aurora A inhibition by Aurora A inhibitor 1 (n = 21) or MLN8237 (n = 15), oocytes show a delay in establishment of a bipolar spindle compared with controls (n = 20), and they can undergo anaphase I without proper bivalent congression to the metaphase I plate. Under Plk4 inhibition by centrinone (n = 10), oocytes eventually form a bipolar spindle. Similarly, as a result of Plk1 inhibition using BI2536 (n = 15), oocytes exhibit a delay in establishing a metaphase plate, and anaphase onset is not observed within 17 h. (F) Prometaphase spindle length and width in controls (n = 23) compared with oocytes after inhibition of Plk1 (BI2536, n = 19), Plk4 (centrinone, n = 23), or Aurora A (Aurora A inhibitor 1, n = 22; and MLN8237, n = 11). Inhibition of each of the three kinases significantly decreases both prometaphase spindle length and width (***, P < 0.001). Error bars indicate SD of the mean. (G) Percentage of polar body extrusion (PBE) in control oocytes as well as after inhibition of Plk1 (BI2536, n = 19), Plk4 (centrinone, n = 23), or Aurora A (Aurora A inhibitor 1, n = 22; and MLN8237, n = 11). Inhibition of Aurora A or Plk4 decreases the efficiency of polar body extrusion over 17 h of imaging. Inhibition of Plk1 completely prevents polar body extrusion within this time period.