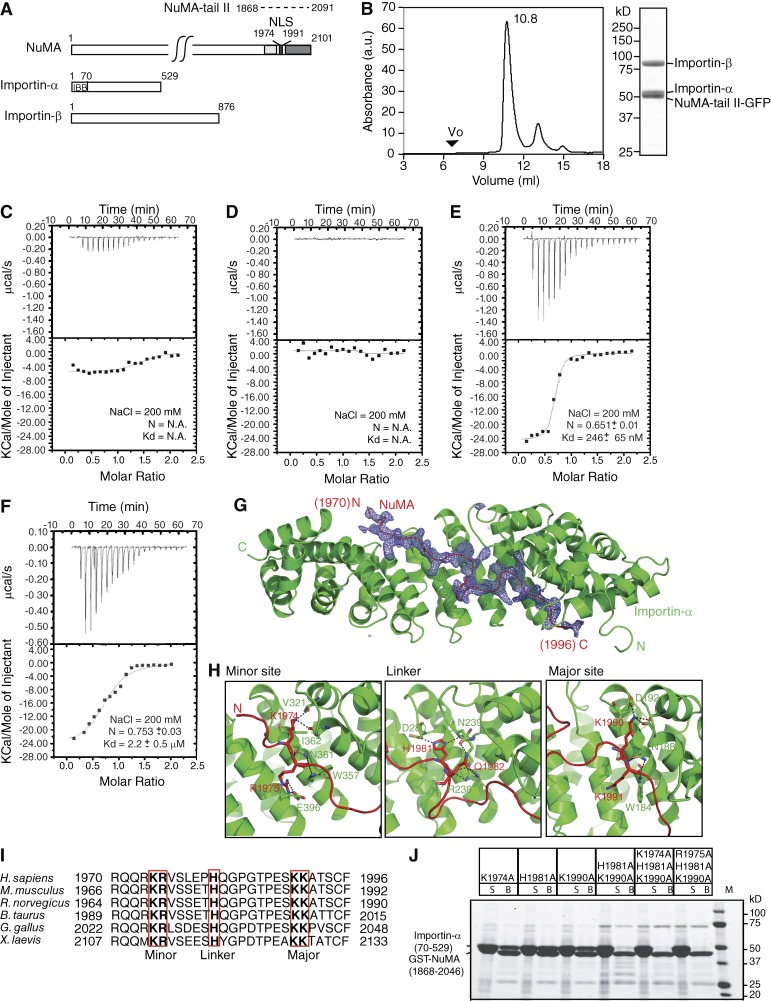
Figure 1.
Biochemical and structural characterization of the heterotrimeric NuMA-tail II–Importin-α–Importin-β complex. (A) Domain structures of NuMA, Importin-α, and Importin-β. For NuMA, the microtubule-binding regions suggested by the Merdes and Mapelli groups are shown in light and dark gray, respectively (Haren and Merdes, 2002; Gallini et al., 2016). The NLS is colored black. Residue numbers of NuMA-tail II (dotted line) used in biochemical studies are indicated. For Importin-α, the Importin-β binding domain is indicated. (B) Purified recombinant Importin-α, Importin-β, and NuMA-tail II-GFP were mixed and analyzed by SEC. The peak fraction (10.8 ml) was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie blue. SEC (Superdex 200) elution profile for the NuMA-tail II-GFP–Importin-α–Importin-β trimeric complex. The void volume (Vo) of the peak fraction and absorbance (a.u.) at 280 nm for the complex is indicated. (C–F) ITC titration curves (top) and binding isotherms (bottom) of full-length Importin-α (C), full-length Importin-β (D), Importin-α (ΔIBB; E), and 1:1 stoichometric mixture of full-length Importin-α and -β with NuMA-tail II-GFP (F). (G) An omit difference (Fo-Fc) map contoured at 2.5 sigma with a superimposed atomic model of the NuMA (1955–2046)–Importin-α (70–498) complex, showing NuMA in red and Importin-α in green. Residues 1,970 to 1,996 in NuMA are assigned. (H) The three panels highlight the interactions at the minor site, linker region, and major site. (I) Sequence alignment of the NuMA-NLS peptide from different species (numbers represent amino acid positions). The conserved minor-site, linker-region and major-site interacting residues are highlighted by red boxes. (J) GST pull-down assays of Importin-α (70–529) with NuMA-tail mutants. GST-fused NuMA-tail (1,868–2,046) mutants were incubated with recombinant Importin-α. Unbound (S) and bound (B) samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie blue.