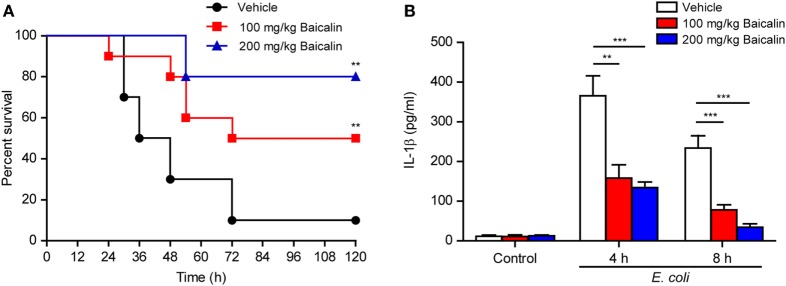
Figure 10.
Baicalin administration prolonged mouse survival in bacterial sepsis. (A) C57BL/6 mice were administered (intragastrically) with baicalin (100 or 200 mg/kg body weight) or vehicle (2% Tween-80 in PBS) once 3 h before peritoneal injection with viable Escherichia coli (2 × 109 CFU/mouse). One hour after the bacterial injection, mice were intragastrically administered with baicalin or vehicle once again. Mouse survival was monitored every 6 h for five consecutive days. Kaplan–Meier survival curves were used to analyze the data (10 mice per group). The significance was evaluated by the log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test. (B) Mice were treated as in panel (A). The serum levels of interleukin (IL)-1β at 4 and 8 h post bacterial infection were measured by cytometric bead array assay (five mice per group). **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.