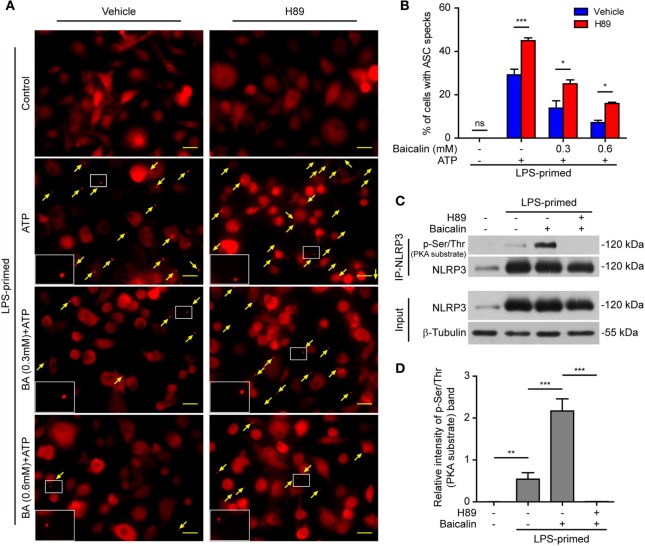
Figure 9.
Baicalin inhibited ASC speck formation by upregulating protein kinase A (PKA) signaling. Bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) were treated as described in Figure 8. (A) Representative immunofluorescence images showing ASC subcellular distribution. Yellow arrows indicate ASC specks. The enlarged insets showed cells with an ASC speck. Scale bars, 20 µm. (B) The ASC speck formation was quantified by the cells with ASC specks relative to the total cells from five random fields each containing ~50 cells. (C) LPS-primed BMDMs were incubated with the PKA inhibitor H89 (20 µM) for 30 min and then treated with baicalin (0.6 mM) for 1 h without adenosine triphosphate (ATP) treatment. NOD-like receptor (NLR) family, pyrin containing domain 3 (NLRP3) immunoprecipitation was analyzed for phosphorylation on PKA-specific sites (p-Ser/Thr PKA substrate). (D) The intensity of p-Ser/Thr phosphorylation on PKA-specific sites of NLRP3 was quantified relative to total NLRP3 in panel (C). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ns, not significant; BA, baicalin.