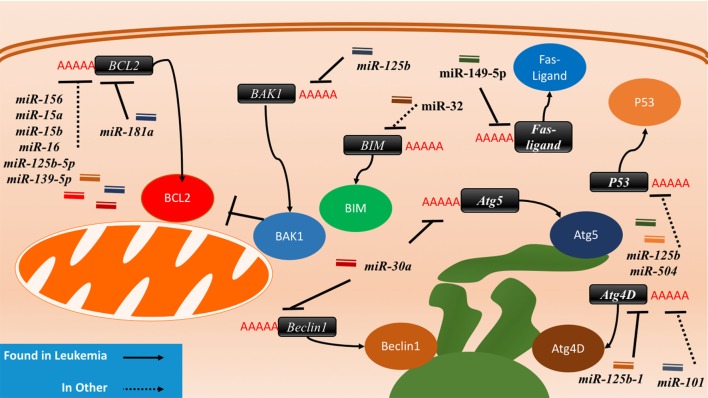
Figure 4.
The interactions between microRNAs (miRNAs) and cell death-related proteins in drug resistant cells. Within the apoptosis cell death mechanism, proteins part of the intrinsic or extrinsic pathway can respond to miRNAs to inhibit apoptosis or reduce their regulatory signaling of apoptosis. BCL2, an anti-apoptosis gene, will gain signaling when the associated miRNAs such as miR-156, miR-15a/b, miR-16, miR-125b-5p, and miR-139-5p are lost in the drug resistant cell. The gain of BAK1 miRNA targeting through miR-125b or the gain of BIM targeting through miR-32 will lead to the same effect as well. The Fas-ligand can also be suppressed by miR-149-5p thus ending extrinsic apoptosis signaling. P53 suppression through miR-125b and miR-504 will prevent apoptosis as well. Dysregulating autophagy through increased targeting may increase drug resistance through the binding of miR-125b and miR-101 on Atg4D. miR-30a is known to inversely correlate with Beclin1 and Atg5 in leukemia cell lines, but less is known about the outcome of this interaction.