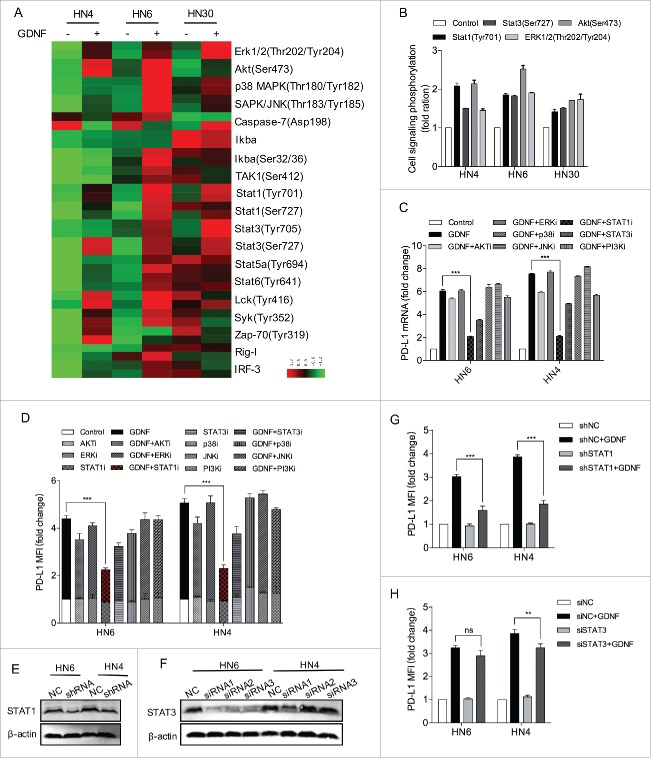
Figure 4.
STAT1 activation regulates GDNF-mediated PD-L1 upregulation. (A) An antibody CHIP assay was used to explore the influence of GDNF on signaling pathways in HNSCC cells. Cell lines were starved for 24 hours and then treated with a negative control or GDNF (30 ng/mL) for 15 min and then harvested for cell signaling analysis. (B) The quantification data are shown for Erk1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204), Akt (Ser473), Stat1 (Tyr701) and Stat3 (Ser727) phosphorylation levels in GDNF-treated cell lines. (C) PD-L1 mRNA determined by real-time PCR analysis in HN6 and HN4 cells pretreated with vehicle control, AKTi (5 μmol/L), ERKi (5 μmol/L), STAT1i (5 μmol/L), STAT3i (5 μmol/L), p38MAPKi (5 μmol/L), JNKi (5 μmol/L) or PI3Ki (5 μmol/L) for 1 hour, flowed by treatment with vehicle control or GDNF (30 ng/mL) for 24 hours. *** means p < 0.001 compared with the control group. (D) PD-L1 protein expression was determined by flow cytometry analysis in HN6 and HN4 cells pretreated with vehicle control, AKTi (5 μmol/L), ERKi (5 μmol/L), STAT1i (5 μmol/L), STAT3i (5 μmol/L), p38MAPKi (5 μmol/L), JNKi (5 μmol/L) or PI3Ki (5 μmol/L) for 1 hour, flowed by treatment with vehicle control or GDNF (30 ng/mL) for 48 hours. *** means p < 0.001 compared with the control group. (E) STAT1 protein expression was evaluated by WB after shRNA transfection. β-actin was used as a loading control. (F) STAT3 protein expression was evaluated by WB after siRNA transfection. β-actin was used as a loading control. (G) A flow cytometry assay indicated that GDNF-mediated PD-L1 protein upregulation despite STAT3 knockdown. Cells lines were treated with SiNC or SiSTAT3 for 48 hours and then treated with vehicle control or GDNF (30 ng/mL) for 48 hours. (H) A flow cytometry assay indicated that GDNF-mediated PD-L1 protein upregulation was diminished when STAT1 was knocked down. ShNC and shSTAT1 cell lines were treated with vehicle control or GDNF (30 ng/mL) for 48 hours.