Figure 2.
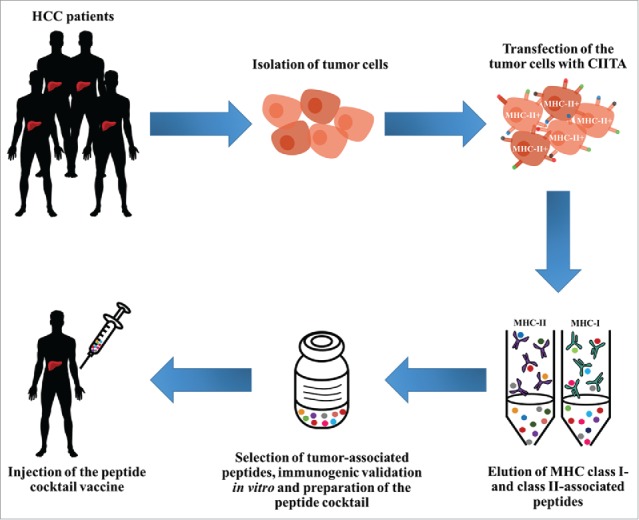
From bench to bedside: CIITA-modified tumor cells as source of MHC-II-bound tumor peptides for innovative vaccines. Human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells isolated from tumor-bearing patients are modified by genetic transfer of CIITA. Resulting MHC-II-positive cells are then submitted to purification of MHC-II-peptide complexes following the XPRESIDENT™ protocol,44 in association with purification of MHC-I-bound peptides. Peptides bound to both MHC-II and MHC-I are eluted, purified, sequenced and selected on the basis of their specific expression on tumor cells and not normal liver cells or tumors of different histotype. Immunogenic validation of selected tumor-specific peptides is performed in vitro by stimulation of lymphocytes from tumor-bearing patients sharing the MHC genotype from which peptides have been purified. Most immunogenic MHC-II- and MHC-I-bound tumor peptides will compose the “peptide vaccine cocktail” that will be injected into HCC patients. For additional detail on the vaccination strategy and clinical trial see also http://www.hepavac.eu/.
