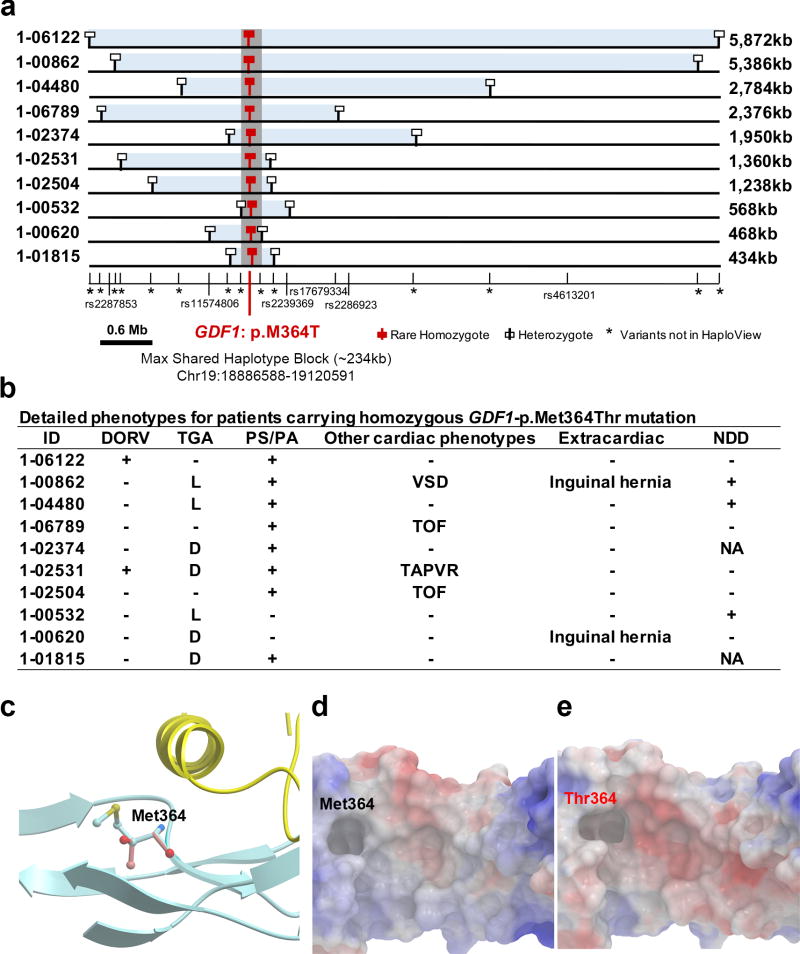
Figure 2. Phenotypes and shared haplotypes among homozygotes for GDF1-p.Met364Thr.
(a). Extent of homozygous SNPs flanking homozygous GDF1-p.Met364Thr genotypes. A 5.9 Mb segment of chromosome 19 extending across the location of the homozygous GDF1-p.Met364Thr mutation (denoted by red square) in each unrelated subject is depicted. At the bottom, tick marks indicate location of all SNPs found by exome sequencing among Ashkenazim in cases. Known SNPs are shown via their rs identifiers. Allele frequencies of novel SNPs are indicated by asterisks. The closest heterozygous SNP to either side of the GDF1-p.Met364Thr in each subject is shown as a white square; all SNPs between these two heterozygous SNPs, encompassed by the light blue bar, are homozygous for the same allele seen in other subjects, consistent with the p.Met364Thr variant being identical by descent among all subjects. The length of each homozygous segment is indicated at the right of the panel. The maximum length of the homozygous segment shared by all subjects is 234 kb (shown as grey vertical bar), consistent with the mutation having been introduced into a shared ancestor many generations ago. (b). Cardiac and extracardiac phenotypes of GDF1-p.Met364Thr homozygotes. Present phenotypes are denoted with ‘+’, those absent with ‘−’, and those unavailable for testing with ‘NA’ (c). Ribbon diagram of part of GDF1 homodimer containing p.Met364. The hydrophobic helix from one subunit (yellow) sits above p.Met364 on the other subunit (blue). (d). Space filling model of the segment of GDF1 containing the wild-type p.Met364 showing surface electrostatic charge (blue=positive, red=negative). (e). Surface electrostatic charge of the segment containing mutant p.Thr364. Compared to wild-type, the mutant peptide shows a more negatively charged cavity.