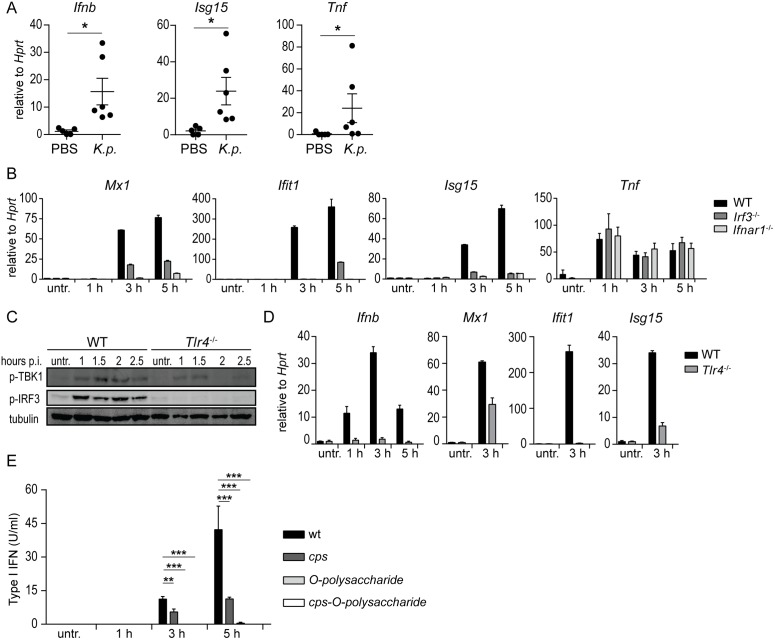
Fig 2. Induction of type I IFN signaling in macrophages by K. pneumoniae is dependent on Irf3 and Tlr4, and the bacterial capsule polysaccharide (CPS) and LPS O-polysaccharide.
(A) Mouse alveolar macrophages isolated from K. pneumoniae-infected (intranasal, 5 x 104 CFU) or PBS-treated WT mice were analyzed for expression of Ifnb, Isg15 and Tnf using qPCR 24 h p.i. (n = 5, PBS; n = 6, infection). (B) BMDMs from WT, Irf3-/- and Ifnar1-/- mice were left untreated or infected for indicated time points with K. pneumoniae (MOI = 70), and mRNA levels of Mx1, Ifit1, Isg15 and Tnf were determined by qPCR. Error bars, mean ± SEM (n > 3). (C, D) WT and Tlr4-/- BMDMs were infected as in (B) for indicated time points, or left untreated. Phospho-TBK1 (p-TBK1), phospho-IRF3 (p-IRF3) and tubulin (loading control) were detected in whole cell extracts by Western blotting (E), and Ifnb, Mx1, Ifit1 and Isg15 mRNA levels were quantitated by qPCR (D). (E) BMDMs were infected as in (B) with a cps, O-polysaccharide, and double cps-O-polysaccharide K. pneumoniae mutants for indicated time points, or left untreated, and type I IFN levels in the supernatants were quantitated using bioassays. Statistical evaluation in (A) and (E): unpaired Student’s t test; error bars, mean ± SEM (n > 3); *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.