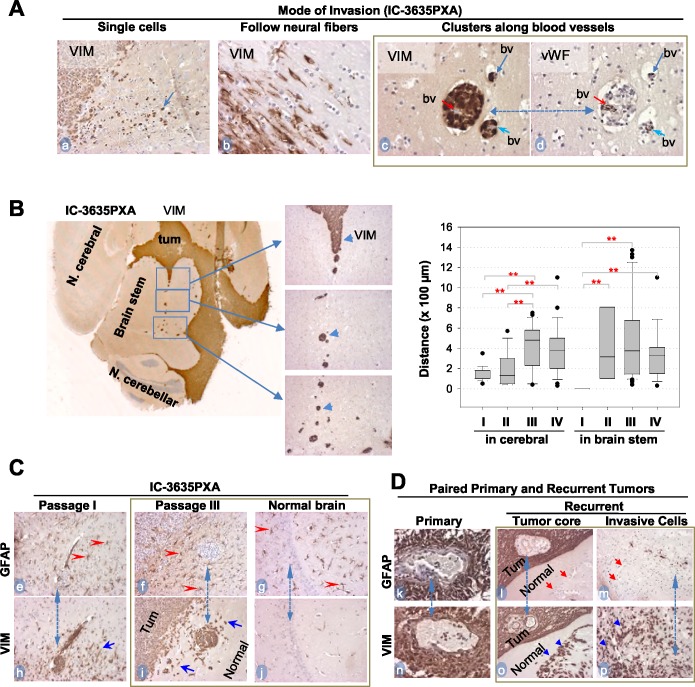
Figure 5. In vivo tumor invasion and host responses detected with IHC.
(A) Modes of IC-3635PXA invasion in mouse brains. Tumor cells positively stained with Vimentin (VIM) (arrows, a-c), and blood vessels (bv) with vWF (d). Same area in two consecutive sections was included (c and d, dotted line with dual arrow heads). (B) Images showing long-range perivascular invasion (left panel) and quantitative analysis perivascular migration (right panel) (** P< 0.01). Tumor cells positively stained with VIM (arrow heads). (C) IHC showing mutually exclusive positivity between GFAP (marker for mature glial cells) (red arrowheads, e-g) and VIM in tumor mass (Tum) and in invasive satellites and single cells (blue arrowheads, h and i). Note presence of reactive astrocytes in normal brain tissues (g) without presence of tumor cells (j). Matched areas in consecutive sections were used (dotted line with dual arrow heads) for GFAP and VIM staining (magnification x 20). (D) IHC of paired primary and recurrent PA confirming invasive cells to be GFAP- (red arrow, l and m) and VIM+ (blue arrowheads, o and p) Magnification (x40: k and n; x20: l, m, o, p).