Figure 1. IL-13 increases Bcl-2 and Bik expression and suppressing Bcl-2 induces apoptosis.
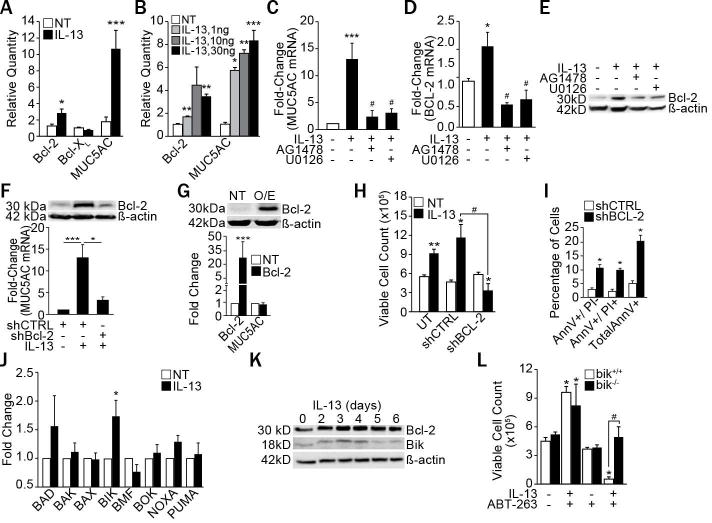
(A) Bcl-2, Bcl-XL and MUC5AC mRNA levels in differentiated primary HAECs from 10 different subjects treated with IL-13 (10 ng/ml) for 5 d and analyzed by qRT-PCR. (B) Primary HAECs treated with the indicated concentrations of IL-13 were analyzed for Bcl-2 and MUC5AC mRNA levels. Quantification of MUC5AC mRNA (C), Bcl-2 mRNA (D), and Bcl-2 protein (E) in HAECs treated with IL-13 (10 ng/ml) and with either EGFR inhibitor, AG1478 (1 μM) or with ERK1/2 inhibitor, U0126 (1 μM). (F) MUC5AC mRNA and Bcl-2 protein levels in HAECs transfected with shBcl-2 or shCTRL, and treated with IL-13. (G) Bcl-2 protein and MUC5AC mRNA levels in Bcl-2 overexpressing (Bcl-2 O/E) compared with untransfected (UT) cells. (H) Number of viable HAECs recovered after IL-13 treatment of untransfected, shCTRL-, or shBcl-2-transfected cells. (I) Annexin V (AnnV) and propidium iodide (PI) positivity of shCTRL- or shBcl-2-transfected HAECs as analyzed by flow cytometry following IL-13 treatment. (J) Expression levels of pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members in differentiated primary HAECs treated with IL-13 compared to non-treated (NT) controls and analyzed by qRT-PCR (n=8 HAECs from different subjects). (K) Time-course of Bcl-2 and Bik protein levels in HAECs treated with IL-13. (L) Number of viable bik−/− and bik+/+ MAECs 48 h after IL-13 and ABT-263 treatment. Data shown as mean±SEM with n≥3 unless otherwise indicated; #p<0.05 between cells treated with IL-13 and ABT-263. *p<0.05; **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
