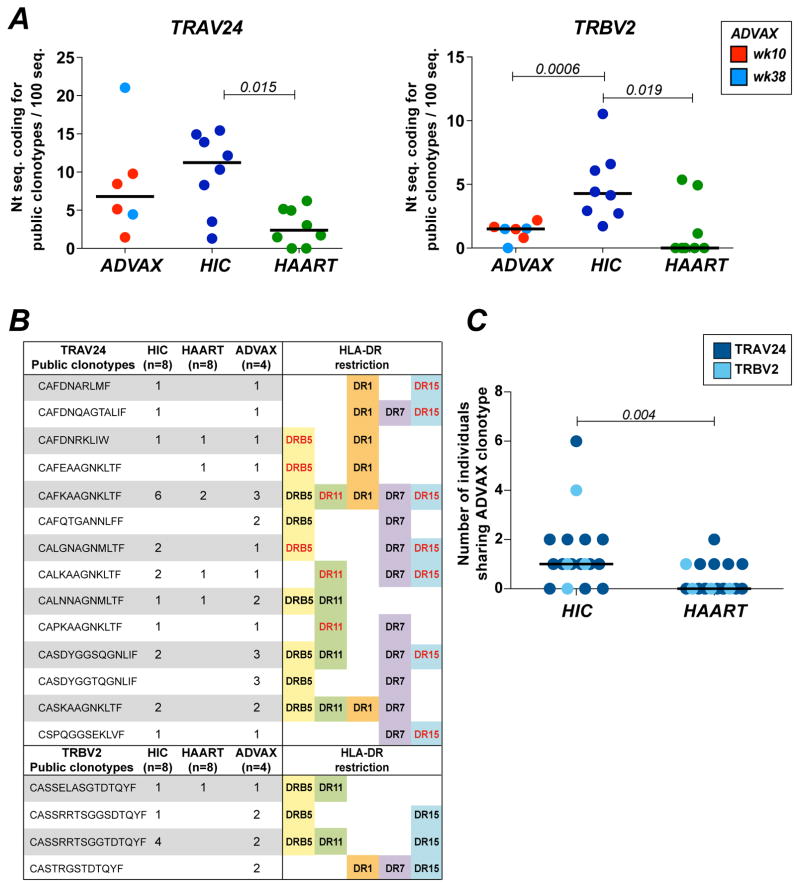
Figure 5. DNA vaccination induces Gag293-specific public clonotypes shared with HIV controllers.
(A) Frequency of nucleotide sequences coding for TRAV24 (left) and TRBV2 (right) public clonotypes, normalized to 100 sequences. Public clonotypes are defined as identical CDR3 a.a. sequences shared by at least 2 individuals. Public clonotype frequencies were compared between ADVAX recipients (week 10, red, TRAV24 n=4, TRBV2 n=4; week 38, light blue, TRAV24 n=2, TRBV2 n=3), HIV Controllers (HIC, dark blue, n=8), and treated patients (HAART, green, n=8).. Significant differences (P < 0.05) obtained with the Mann-Whitney U test are reported.
(B) List public clonotypes found in the TRAV24 and TRBV2 repertoire of Gag293-specific CD4+ T cells from ADVAX recipients. HLA-DR cross-restriction is evidenced by the reporting the diverse MHC II tetramers that could be used to sort a given clonotype, either in the present vaccine study (black type) or in the previous HIV controller study (red type) (22).
(C) Clonotypic repertoire overlap between groups was evaluated by counting for each public clonotype found in vaccinees the number of patients in the HIC (left) and HAART (right) groups who shared this clonotype. TRAV24 (n=14) and TRBV2 (n=4) public clonotypes are represented by dark blue and light blue circles, respectively. The significant difference (P < 0.05) obtained with the Mann-Whitney U test is reported.