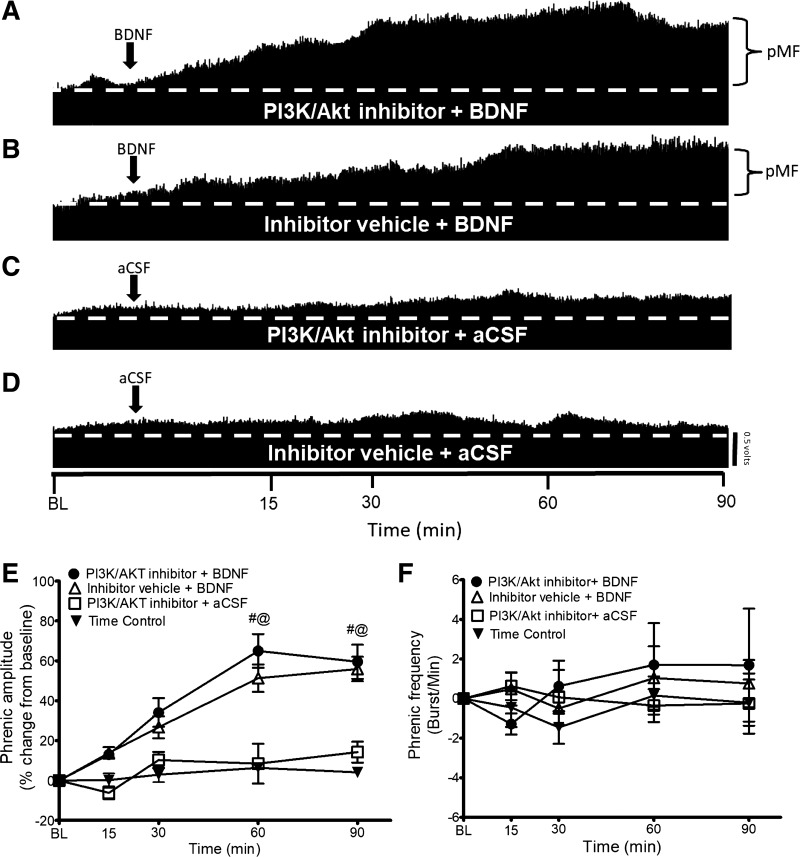
Fig. 2.
A–D: representative traces of compressed integrated phrenic neurograms. BDNF-induced pMF is PI3K/Akt independent since the PI3K/Akt inhibitor PI-828 has no effect. A: intrathecal PI3K/Akt inhibitor PI-828 (100 μM, 12 μl) administration 20 min before intrathecal BDNF does not affect pMF. B: intrathecal BDNF after the inhibitor vehicle (20% DMSO-80% saline) elicits pMF. C: PI3K/Akt inhibitor + BDNF vehicle (aCSF) does not exhibit pMF. D: intrathecal administration of inhibitor vehicle + aCSF does not exhibit pMF. E: group data for phrenic burst amplitude expressed as % change from baseline. PI3K/Akt inhibitor + BDNF (n = 5), Inhibitor Vehicle + BDNF (n = 10), PI3K/Akt inhibitor + aCSF (n = 5), and Time Control (n = 8) groups were compared to determine significance between groups. There were no significant differences at any time between PI3K/Akt inhibitor + BDNF- and inhibitor vehicle + BDNF-treated rats. There were no significant differences at any time between PI3K/Akt inhibitor + aCSF and Inhibitor Vehicle + aCSF groups. There were significant differences between the PI3K/Akt inhibitor + BDNF and Inhibitor Vehicle + BDNF groups vs. PI3K/Akt inhibitor + aCSF and Time Control groups at 60 and 90 min after BDNF. Significance is P ≤ 0.05: #significantly different from PI3K/Akt inhibitor PI-828 + aCSF; @significantly different from Inhibitor Vehicle + aCSF. F: group data for phrenic frequency; there were no significant differences in frequency between any groups at any time.