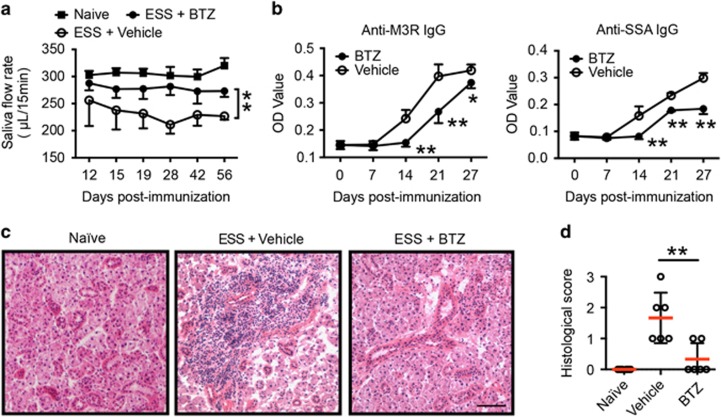
Figure 2.
BTZ treatment ameliorates ESS development. ESS mice were induced with immunization of SG proteins and injected with either vehicle or BTZ intravenously twice a week for 7 weeks, starting at 3 days after the first immunization. (a) The saliva flow rates were monitored in naive or SG immunized mice treated with vehicle or BTZ. Mice immunized with adjuvant alone served as naive controls. Values between the vehicle- and BTZ-treated groups were compared, with an asterisk (*) indicating the differences (n=5–11 per group, mean±s.d., *P<0.05, **P<0.01). (b) Levels of IgG against M3R (left) and SSA (right) in the serum of vehicle- or BTZ-treated mice were measured by an ELISA assay (n=5~8 per group, mean±s.d., *P<0.05, **P<0.01). (c, d) Immunized mice were treated with vehicle or BTZ for 7 weeks. The mice were killed for histological analysis at 15 weeks after the first immunization. (c) Representative images of H&E staining of SG tissue sections from naive, vehicle- or BTZ-treated mice showing glandular infiltration (scale bar=20 μm). (d) Histological scores were assessed based on lymphocytic infiltration in the SG (**P<0.01). BTZ, bortezomib; ESS, experimental Sjögren’s syndrome; SG, salivary gland; SSA, Sjögren’s syndrome-related antigen A.