Figure 4.
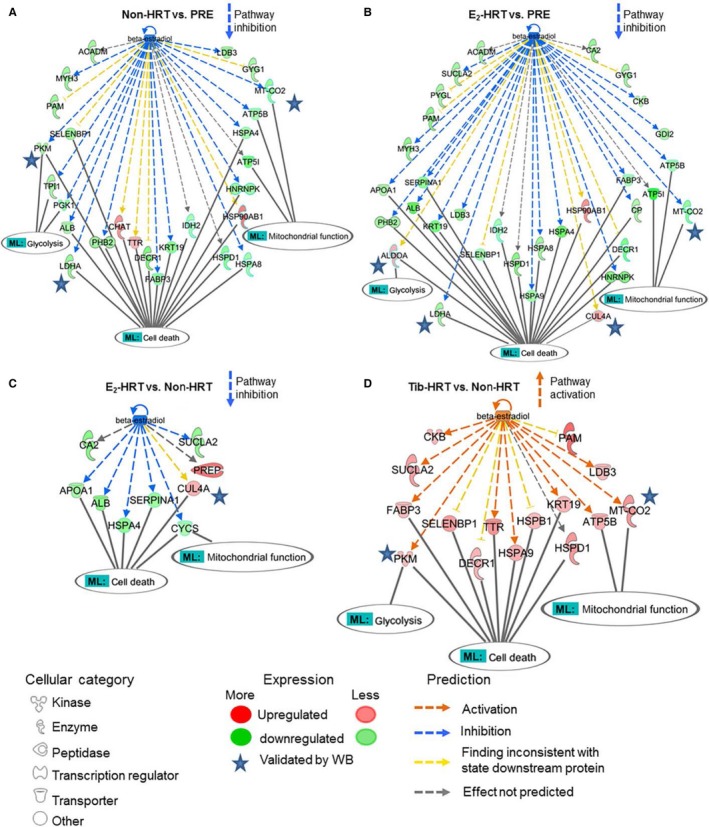
Comparative analysis of 17β‐estradiol (E2) regulated differentially expressed proteins (DEPs). (A) The DEPs identified in postmenopausal women without hormone replacement (HRT) in comparison with premenopausal women (non‐HRT vs. PRE). (B) Comparison of E2‐regulated DEPs among postmenopausal E2‐HRT users and premenopausal women (E2‐HRT vs. PRE). (C) Comparison of the E2‐regulated DEPs in postmenopausal E2‐HRT users and their nonusing cotwins (E2‐HRT vs. non‐HRT). (D) E2‐regulated DEPs in the postmenopausal Tib‐HRT users in comparison with their nonusing cotwins (Tib‐HRT vs. non‐HRT). The DEPs associated with the predicted downstream functions related to cell death and glycolysis as well as associated with mitochondrial functions are presented. Blue stars indicate DEPs with expression change validated by semi‐quantitative immunoblotting. ML = my lists are assembled by including all the observed DEPs involved in the corresponding pathways in any of the four conditions. ML: cell death and ML: glycolysis, originate from the analysis presented in the Fig. 3D, while ML: mitochondrial functions from the canonical pathways oxidative phosphorylation and mitochondrial dysfunction presented in the Fig. 2B. Arrows indicate the predicted inhibition or activation of the entire cascade.
