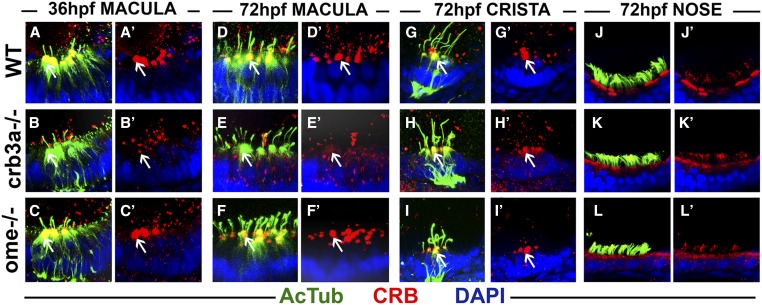
Figure 3.
Crumbs expression in crb3a mutants at early stages of development. Confocal images of whole-mount cilia staining with anti-acetylated tubulin (AcTub) (green) and anti-CRB antibody (red). (A–C’) Staining of the otic vesicle at 36 h postfertilization (hpf). Crumbs proteins localize to the cilia base in the wild-type (WT) (A and A’) and ome−/− mutants (C and C’), but are absent in crb3a−/− mutant homozygotes (B and B’). At 72 hpf, Crumbs proteins still localize to the cilia base in maculae of WT animals (D and D’) and ome−/− mutants (F and F’), but very little signal is seen in crb3a−/− mutants (E and E’). No obvious differences are found in the localization of Crumbs proteins in the cristae of ome−/− (I and I’), crb3a−/− (H and H’), and WT individuals (G and G’). The localization patterns of Crumbs proteins in nasal pits of WT (J and J’), crb3a−/− mutant (K and K’), and ome−/− mutant (L and L’) animals do not show any obvious differences either. All samples were counterstained with DAPI to visualize nuclei. Arrows point to Crumbs signal at the apical surface of hair cells.