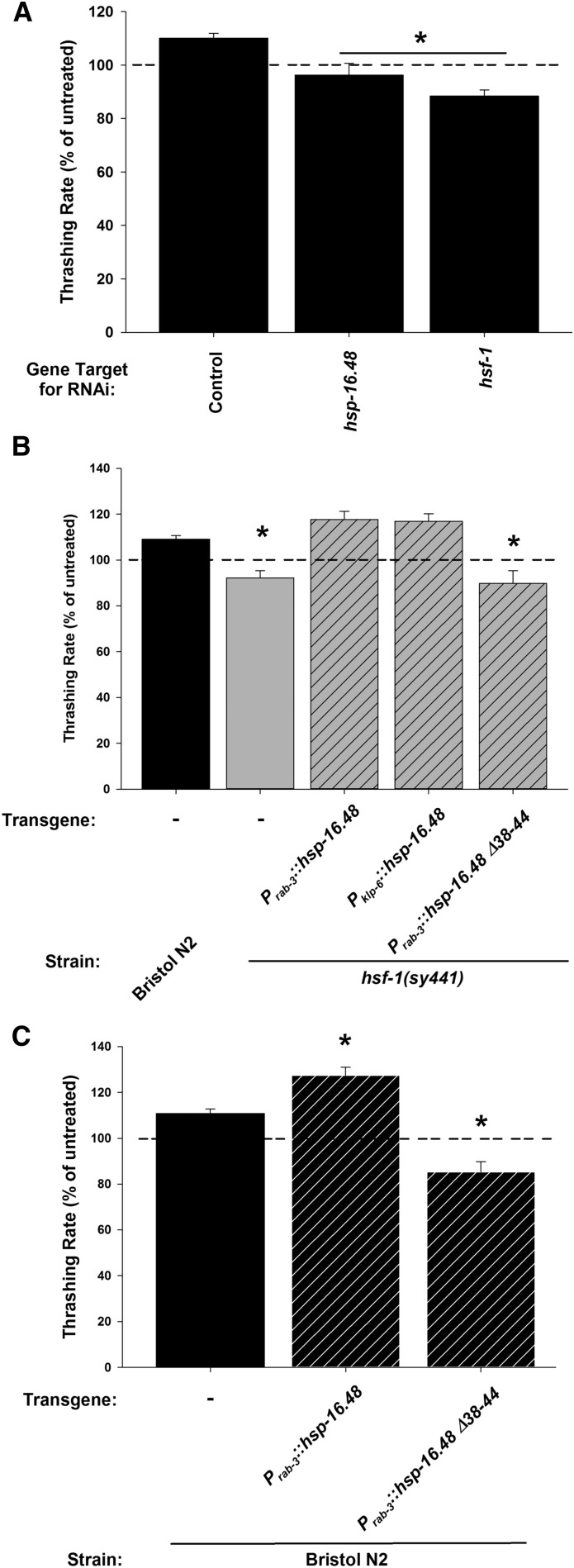
Figure 3.
HSP-16.48 acts downstream of HSF-1 in IL2 neurons. (A) RNA interference (RNAi) knockdown of the small heat shock protein hsp-16.48 statistically phenocopied the ethanol sensitivity of hsf-1 RNAi knockdown in comparison to control. RNAi was performed by feeding where controls were fed empty vector. n.s. = not significant. (B) Either pan-neuronal (Prab-3) or IL2-specific (Pklp-6) expression of hsp-16.48 rescued the hsf-1(sy441) mutant phenotype. Expression of an hsp-16.48 truncation mutant (+Δ38-44) was unable to rescue. (C) Overexpression of hsp-16.48 in Bristol N2 worms enhanced the ethanol stimulation of locomotion to a significantly greater extent, whereas the hsp-16.48 truncation mutant (+Δ38-44) blocked the ethanol enhancement of locomotion. For (A–C), data are expressed normalized to untreated controls. For each experiment, exposure to ethanol enhanced the locomotion rate of RNAi control or Bristol N2 worms (Mann–Whitney U-test; P < 0.05). * indicates significant difference in comparison to treated RNAi control or Bristol N2. Comparisons were made by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc comparisons [P < 0.001; N = 10 (A), 30 (B) and 20 (C) for each condition]. Bristol N2 worms are depicted in black, hsf-1(sy441) in gray. Hatching indicates transgenic expression (transgene and promoter indicated below graph).