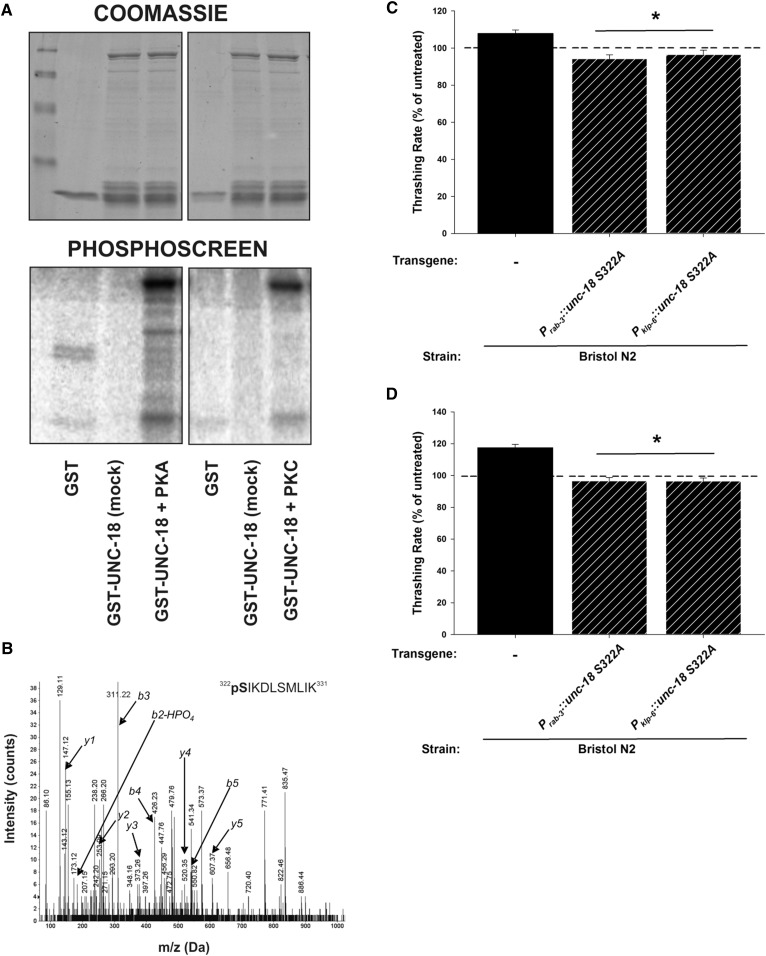
Figure 6.
UNC-18 is phosphorylated by protein kinase A, and phosphorylation of UNC-18 Ser322 is required for both ethanol and forskolin-dependent stimulation of locomotion. (A) Recombinant UNC-18 protein (GST-UNC-18) was incubated with 32P-labeled ATP in the absence (mock) or presence of either protein kinase C (+PKC) or protein kinase A (+PKA). Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and phosphorylation was determined by PhosphorImager (Phosphoscreen). Coomassie staining indicates equal protein loading. (B) Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry data positively indicating phosphorylation of Ser322 of UNC-18 in PKA-phosphorylated protein samples. (C) Pan-neuronal (Punc-18) or IL2-specific (Pklp-6) expression of a phospho-null mutation of a PKA-phosphorylation site of unc-18 (S322A) in Bristol N2 blocked the ethanol-dependent stimulation of locomotion. (D) Pan-neuronal (Punc-18) or IL2-specific (Pklp-6) expression of a phospho-null mutation of a PKA-phosphorylation site of unc-18 (S322A) in Bristol N2 blocked the forskolin-dependent stimulation of locomotion. For (C and D), data are expressed normalized to untreated controls. Exposure to ethanol or forskolin enhanced the locomotion rate of Bristol N2 worms (Mann–Whitney U-test; P < 0.05). * indicates significant difference in comparison to treated Bristol N2. Comparisons were made by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc comparisons (P < 0.001; N = 30 for each condition). Bristol N2 worms are depicted in black. Hatching indicates transgenic expression (transgene and promoter indicated below graph).