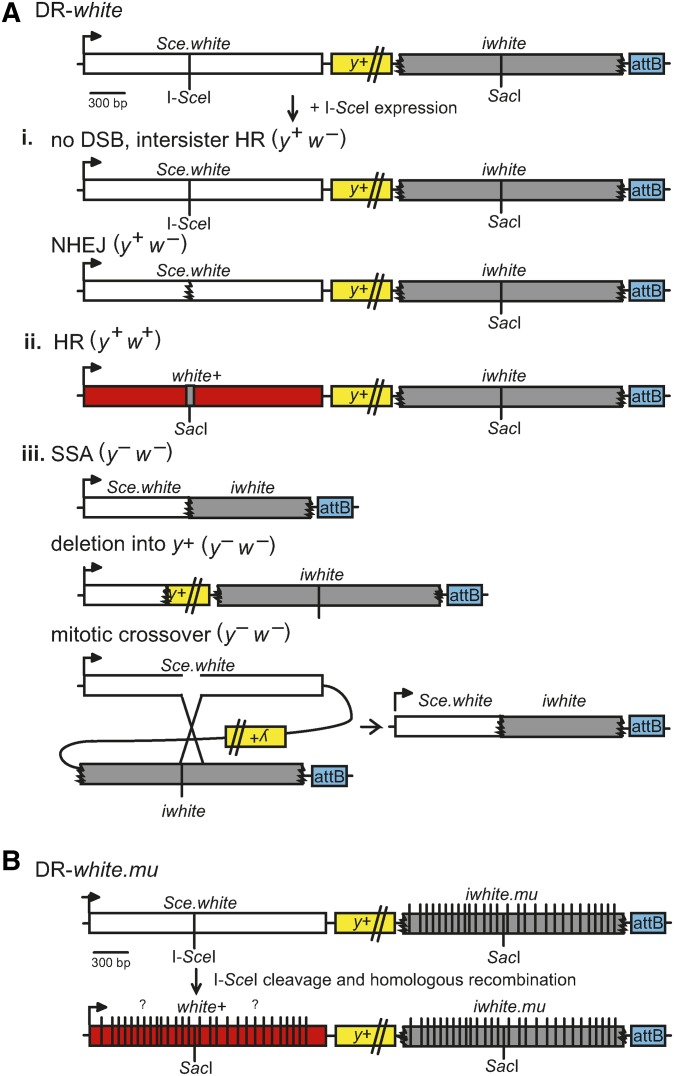
Figure 2.
DR-white and DR-white.mu DSB repair assays. (A) The DR-white assay contains two nonfunctional direct repeats of the white gene. The first repeat, Sce.white, is nonfunctional due to the insertion of an I-SceI recognition sequence into the wild-type SacI recognition sequence of white cDNA resulting in a defective white gene. The second repeat, iwhite, is nonfunctional due to 5′ and 3′ truncations and serves as a homologous donor sequence for repair. DR-white is targeted using the attB sequence (blue) and integration is confirmed using yellow (y+) transgene expression. DR-white flies are crossed with flies containing an I-SceI transgene, in which expression results in DSB formation at the I-SceI recognition sequence. Repair events are observed by crossing these males to y w tester females; progeny of this cross represent single DSB repair events of the male germline. One of three phenotypes will result depending on the repair. (i) White-eyed progeny (y+ w−) suggest no DSB, intersister HR, or repair by NHEJ with processing, resulting in loss of the I-SceI recognition sequence. NHEJ with processing can be identified through molecular analysis. (ii) Repair by HR results in restoration of the wild-type SacI site from the iwhite donor sequence and a red-eyed fly (y+ w+). (iii) Yellow-bodied, white-eyed (y− w−) progeny indicates repair by SSA, mitotic crossover event (indistinguishable from SSA), or an aberrant repair event that impedes y+ expression, such as a deletion into the y+ transgene. (B) The DR-white.mu assay includes the incorporation of 28 silent polymorphisms on the iwhite.mu donor sequence, resulting in a 1.4% increase of sequence divergence between the two direct repeats. HR gene conversion of each of the polymorphisms varies from one repair product to the next (indicated by “?”), and can be determined by molecular analyses. DR-white; Direct Repeat of white; DR-white.mu; Direct Repeat of white with mutations; DSB, double-strand break; HR, homologous recombination; NHEJ, nonhomologous end-joining; SSA, single-strand annealing.