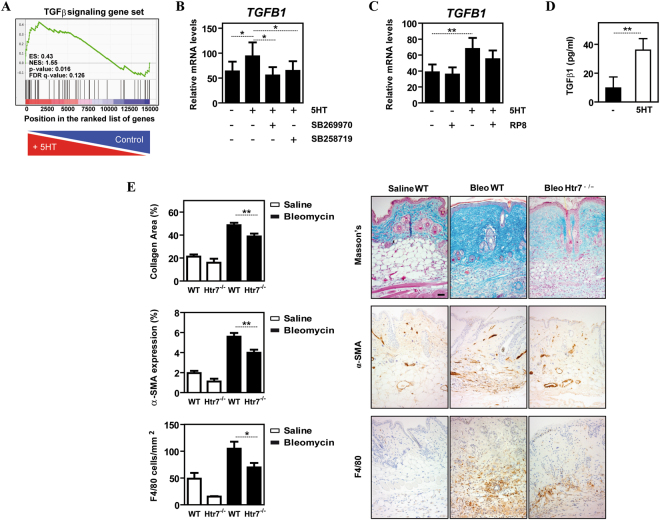
Figure 6.
5-HT7R engagement promotes the acquisition of a pro-fibrotic gene signature in human macrophages and contributes to pathology-associated parameters in a mouse model of skin fibrosis. (A) GSEA on the “t statistic-ranked” list of genes obtained from the 5-HT-treated M-MØ versus M-MØ limma analysis, using the “TGFβ signaling” gene set. Black vertical lines indicate the position of each of the genes included within the “TGFβ signaling” Hallmark gene set. (B) Relative expression of TGFB1 mRNA in non-treated M-MØ (-) or M-MØ exposed to 5-HT (5HT, 6 h) in the absence or in the presence of the 5-HT7R antagonists SB269970 or SB258719. Results are expressed as the TGFB1 mRNA level relative to the TBP mRNA level in the same sample (n = 6; *p < 0.05). (C) Relative expression of TGFB1 mRNA in non-treated M-MØ (-) or M-MØ exposed to 5-HT (5HT, 6 h) in the absence or in the presence of the PKA inhibitor RP8. Results are expressed as the TGFB1 mRNA level relative to the TBP and HPRT1 mRNA level in the same sample (n = 6; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01). (D) Production of TGFβ1 by non-treated M-MØ (-) or M-MØ treated with 5-HT (5HT) for 24 h. (n = 3; **p < 0.01). (E) Fibrosis was measured as the collagen Masson stained area (upper panel), immunohistochemistry analysis of activated fibroblasts (α-SMA+, middle panel) and number of F4/80+ cells per area (lower panel), in lesional skin from saline- or bleomycin-treated control and Htr7 −/− mice. Shown are the mean and SEM of three independent experiments with 10 mice per group. Statistical significance was evaluated using Mann-Whitney U-test, (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01). Representative skin sections stained are shown (bar, 50 μM).