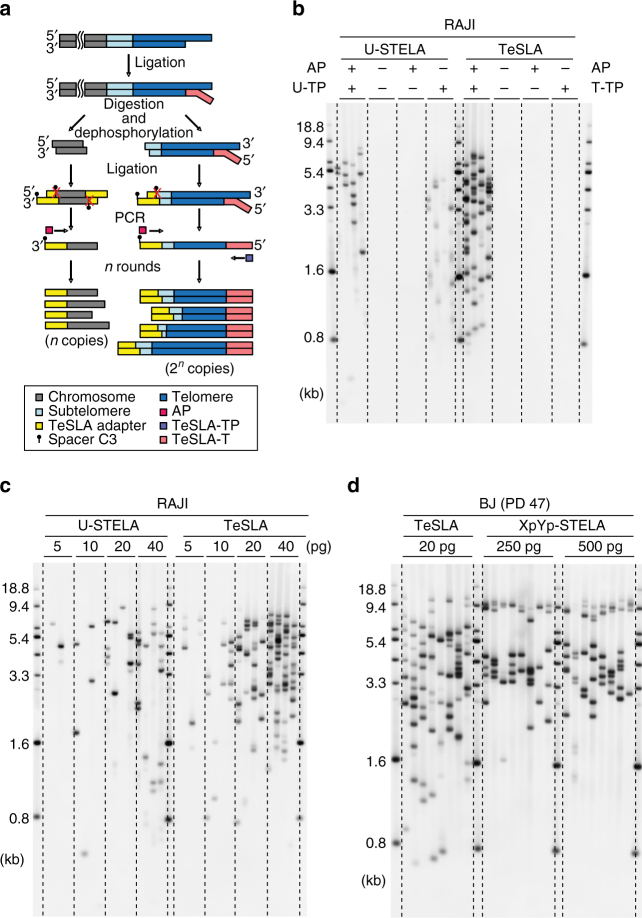
Fig. 1.
Overview of Telomere Shortest Length Assay (TeSLA) and comparison to Universal STELA (U-STELA) and XpYp STELA. a Schematic of overall TeSLA methods. Extracted genomic DNA is ligated with TeSLA-Ts (each TeSLA-T contains seven nucleotides of telomeric C-rich repeats at the 3′ end) at the overhangs of telomeres and then digested with a restriction enzyme panel. Digested DNA is subsequently ligated with doubled-stranded TeSLA adapters at the proximal end of telomeres and genomic DNA fragments. After adapter ligation, PCR is performed to amplify ligated telomeric DNA. b About 40 pg of DNA from RAJI cells was used in each U-STELA and TeSLA reaction to test specificity of primers for telomere amplification and was tested as indicated (AP, adapter primer; U-TP, U-STELA teltail primer; T-TP, TeSLA-TP). c The sensitivity of U-STELA and TeSLA was compared by serial dilution of DNA from RAJI cells from 5 to 40 pg. d Using TeSLA (20 pg DNA for each reaction) and XpYp STELA (250 and 500 pg of DNA for each reaction) to detect TL in BJ cells