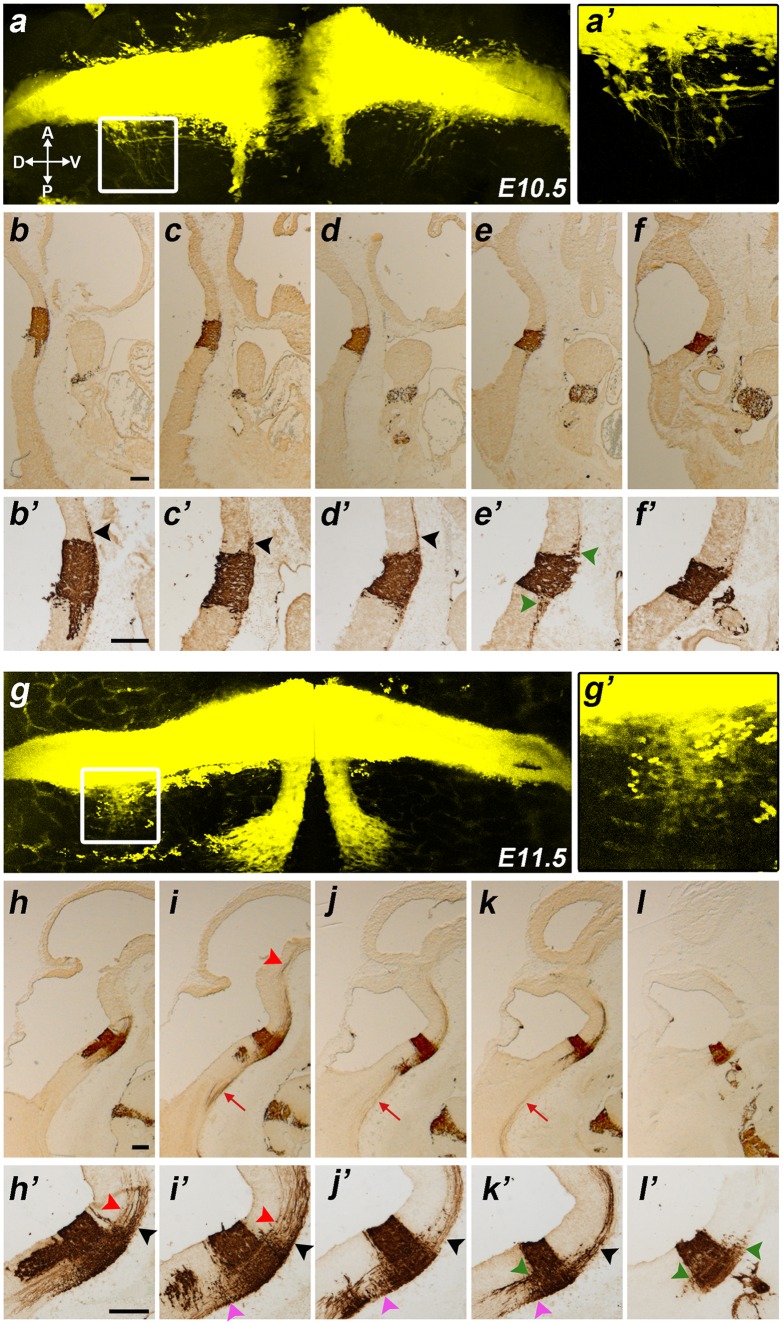
Fig. 1.
Results at E10.5, E11.5. a, g Hindbrain flat mounts of b1r4-Cre/YFP double heterozygote embryos at E10.5 (a) and E11.5 (g). YFP labels rhombomere 4 and r4-derived facial branchiomotor and vestibular neurons. The boxes in a and g indicate the areas shown at high magnification in aʹ and gʹ respectively, illustrating the estimated vestibular neurons invading r5. b–f and h–l Sagittally sectioned b1r4-Cre/YFP specimens at E10.5 (b–f) and E11.5 (h–l); each series is illustrated from medial to lateral levels and was immunoreacted with an antibody against GFP that also recognizes YFP. bʹ–fʹ and hʹ–lʹ Corresponding high-magnification views of rhombomere 4. The facial motor neurons migrate caudally through r5 next to the floor plate and turn laterally within r6 until reaching the alar pial surface where they form the facial nucleus (a, b/bʹ, g, h/hʹ–j/jʹ). The lateral lemniscus tract emerges rostrally from the basal part of r4 and courses obliquely lateralwards and dorsalwards to reach the prepontine alar plate (b/bʹ–d/dʹ, h/hʹ–k/kʹ, black arrowheads). The medial tegmental tract comes out of r4 and crosses the medial tegmentum of the upper hindbrain and reaches the isthmus (h/hʹ, i/iʹ, red arrowheads). R4-derived vestibular neurons (dark green arrowheads) invade r3 (e/eʹ, l/lʹ) and r5 (e/eʹ, k/kʹ, l/lʹ). YFP-positive reticular neurons migrate into r5 (i/iʹ–k/kʹ, pink arrowheads). Other fibres exit the medial basal part of r4 and descend into the spinal cord (i–k, red arrow). For abbreviations see “list of abbreviations”. Scale bar 200 µm