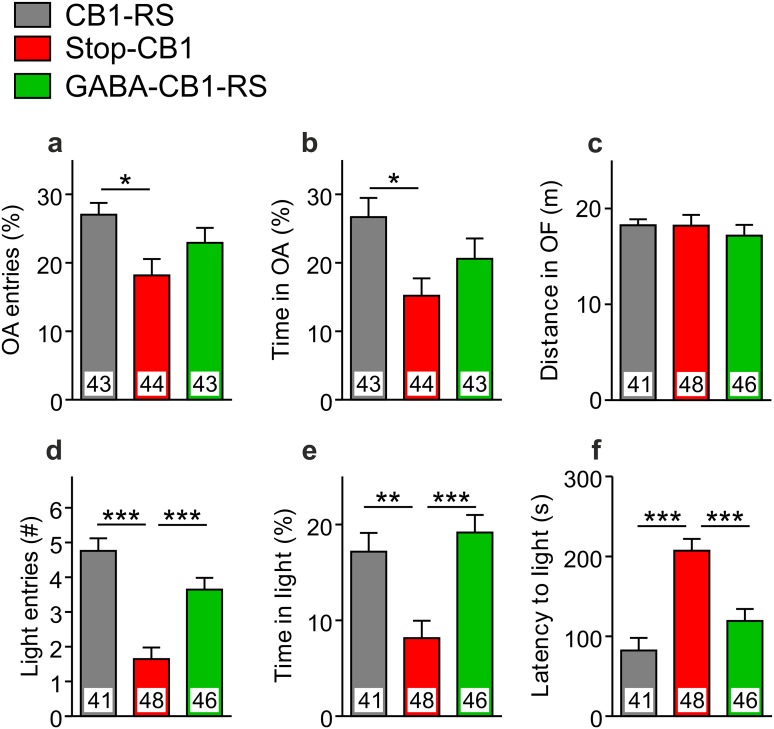
Fig. 8.
Anxiety-like behavior is largely restored to normal by rescue of the CB1 receptor specifically in forebrain GABAergic neurons. In the elevated plus-maze (EPM) test, a the number of entries into the open arms (OA) expressed as percentage of total arm entries and b the time spent in the OA (as percentage of time in total arms) were lower in Stop-CB1 animals than in CB1-RS control animals. GABA-CB1-RS mice had intermediate values and did not differ significantly from both other groups, indicating a partial restoration of the anxiogenic phenotype in GABA-CB1-RS mice. c Distance traveled in the open field (OF) was similar between the three groups. In the light/dark (LD) test, d the number (#) of entries in the light compartment and e the percentage of time spent in the light compartment was similar between CB1-RS and GABA-CB1-RS mice and significantly lower in Stop-CB1 mice, pointing to a full restoration of the anxiogenic phenotype in GABA-CB1-RS mice. f Latency to the first entry of the light compartment was also similar between CB1-RS and GABA-CB1-RS mice and significantly higher in Stop-CB1 mice, confirming that in GABA-CB1-RS mice the phenotype of CB1 receptor deficiency is completely remedied in this paradigm. Data are expressed as mean + SEM (a–c) or covariate-adjusted means + SEM (d–f); animal numbers are indicated in the graphs; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 in one-way ANOVA (for EPM and OF) or univariate ANOVA with OF distance as covariate (for LD), followed by Tukey multiple comparison test; details of statistical analysis in supplementary Table S2