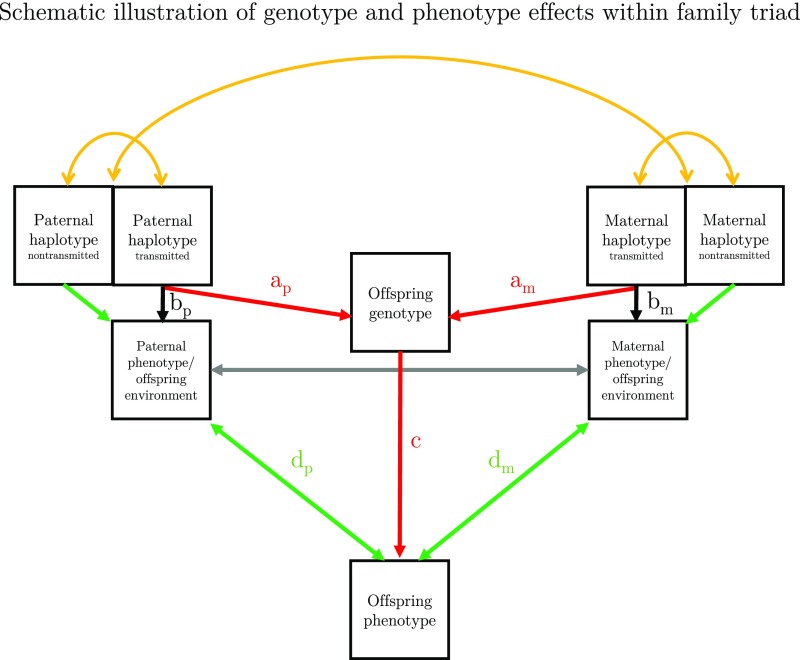
Fig. 3.
Schematic illustration of cross-generational effects within family triad. Because of the lack of parental genotype data, the present study was unable to distinguish passive and evocative gene–environment correlation. Passive gene–environment correlation: am,p × bm,p. Evocative gene–environment correlation: c × bm,p. Offspring phenotype can be influenced by both the transmitted paternal and maternal alleles (red arrows) and by nontransmitted alleles via parental phenotype (green arrows). Provided that paternal, maternal, and offspring genotype and phenotype data were available in a single sample, the effect of parental trait-associated alleles on offspring phenotype independently of genetic sharing between parents and offspring (green arrows) could be estimated (70–72). A testable assumption for investigating these mechanisms is there is no correlation between parental genotypes and between each parent’s haplotypes (i.e., assortative mating) (yellow arrows).