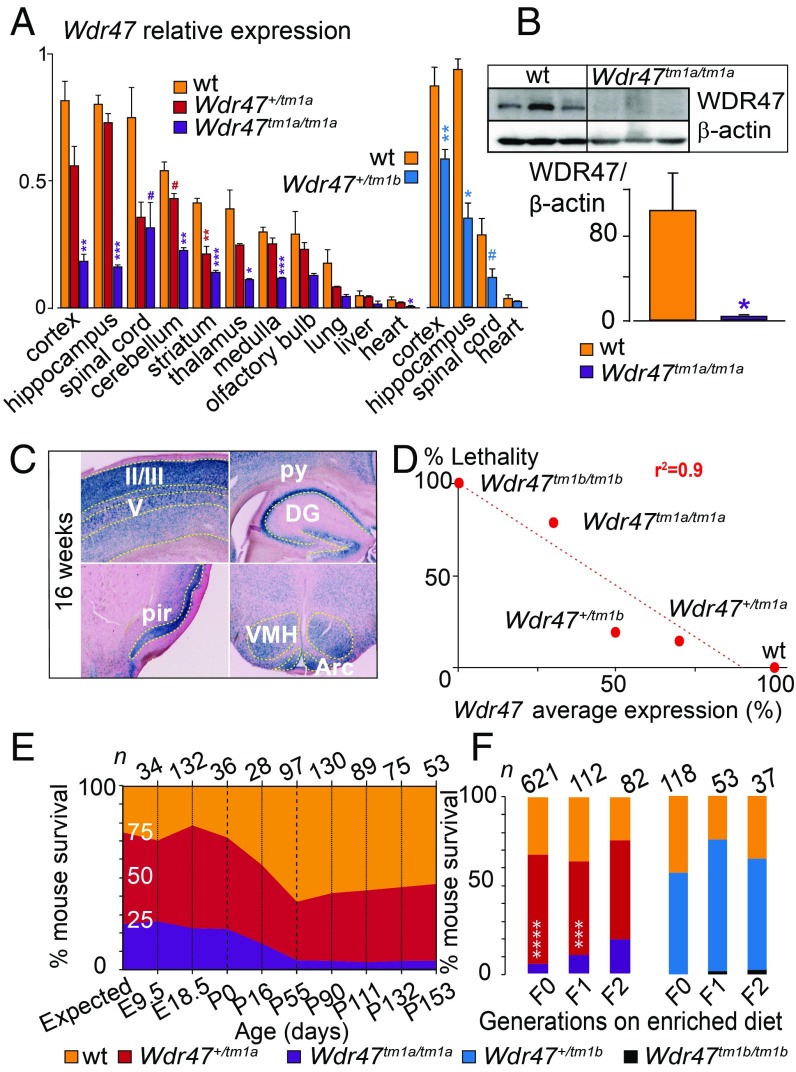
Fig. 2.
Characterization of Wdr47 mouse models. (A) Wdr47 relative expression using qRT-PCR in Wdr47+/tm1a (n = 3), Wdr47tm1a/tm1a (n = 3), and WT (n = 3) across 11 tissues and in Wdr47+/tm1b (n = 3) and WT (n = 3) across 4 tissues (cortex, hippocampus, spinal cord, and heart). Normalization was done using GNAS (guanine nucleotide-binding protein, alpha-stimulating). (B) WDR47 protein profiling in cortex of WT (n = 3) and Wdr47tm1a/tm1a (n = 3). Normalization was done using β-actin. (C) LacZ staining in adult Wdr47+/tm1a across the cortex, pyramidal cells (py), dendate gyrus (DG), piriform cortex (pir), arcuate nucleus (Arc), and ventromedial part (VMH) of the hypothalamus. (Magnification: 20×.) (D) Correlation between Wdr47 average expression and percentage mouse lethality; 843 Wdr47tm1a and 242 Wdr47tm1b were used. A linear regression was fitted (r2 = 0.9). (E) Mouse survival outcome carried out at nine time points both in Wdr47tm1a males and in Wdr47tm1a females. Expected ratio indicates 25% for WT, 50% for Wdr47+/tm1a, and 25% for Wdr47tm1a/tm1a. (F) Mouse survival outcome on supplementation in fortified diet with extra lipids and folic acid (3 vs. 0.7 mg) in Wdr47tm1a and Wdr47tm1b across three generations. Plots are represented as mean + SEM. Statistical analysis was done using Student’s t test (two-tailed; A and B) and χ2 test relative to expected counts (F). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 1E-06; #P < 0.07.