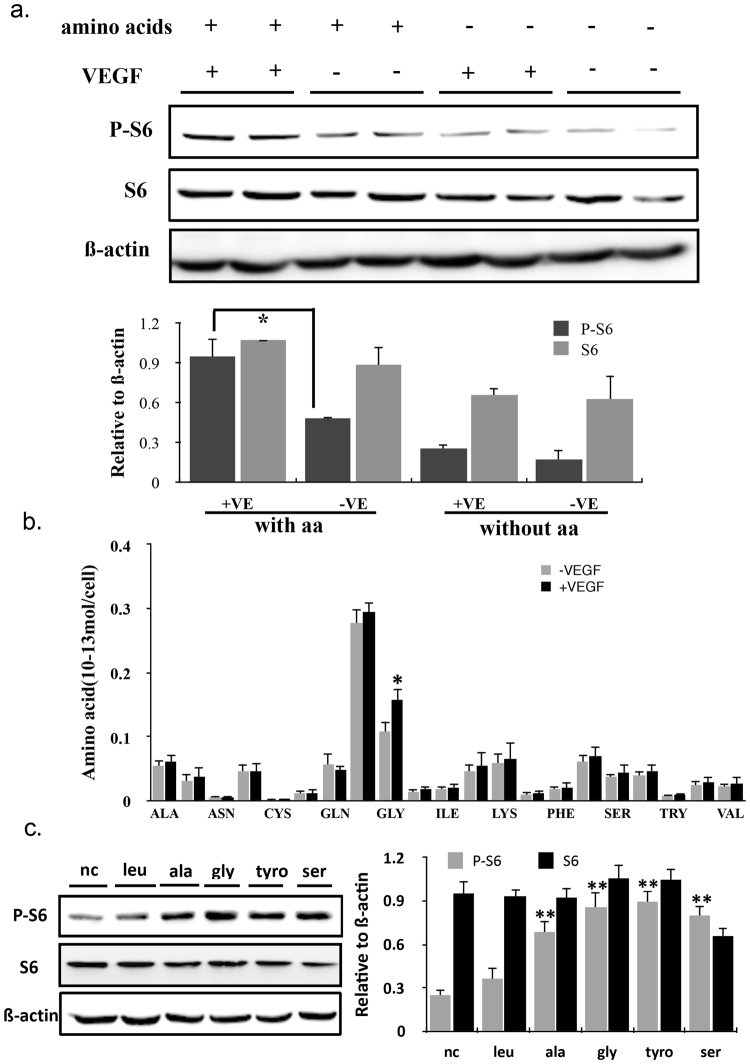
Figure 1.
Glycine was required in the VEGF signals. (a) HUVECs cultured in the medium with or without amino acids were treated with 20 ng/ml VEGF for 24 hours. Immunoblots of P-S6 and S6 were shown. Membranes were reprobed for ß-actin as loading control. Gray values were analyzed by the Image J software and presented in the graph (n = 3). (b) Intracellular content of alanine(Ala), arginine(Arg), asparagine(Asn), aspartic acid(Asp), cysteine(Cys), γ-aminobutyric acid(Gaba), glutamine(Gln), glutamic acid(Glu), glycine(Gly), histidine (His), isoleucine(Ile), leucine(Leu), lysine 37, methionine(Met), phenylalanine(Phe), proline(Pro), serine(Ser), threonine(Thr), tryptophan(Trp), tyrosine(Tyr) and valine(Val) in control and 20 ng/ml VEGF-treated ECs for 24 h. LC-MS was used to detect relative intracellular quantities of amino acids in ECs in the absence and presence of VEGF (n = 3). (c) Immunoblot of total S6 and P-S6 in untreated and different amino acids-treated ECs. The concentration of amino acids: glycine(140 uM), leu(1.33 mM), tyro(1 mM), ala(1 mM), ser(1 mM). The treatment time was 5 h. Quantitative analysis was presented in the graph (n = 3).