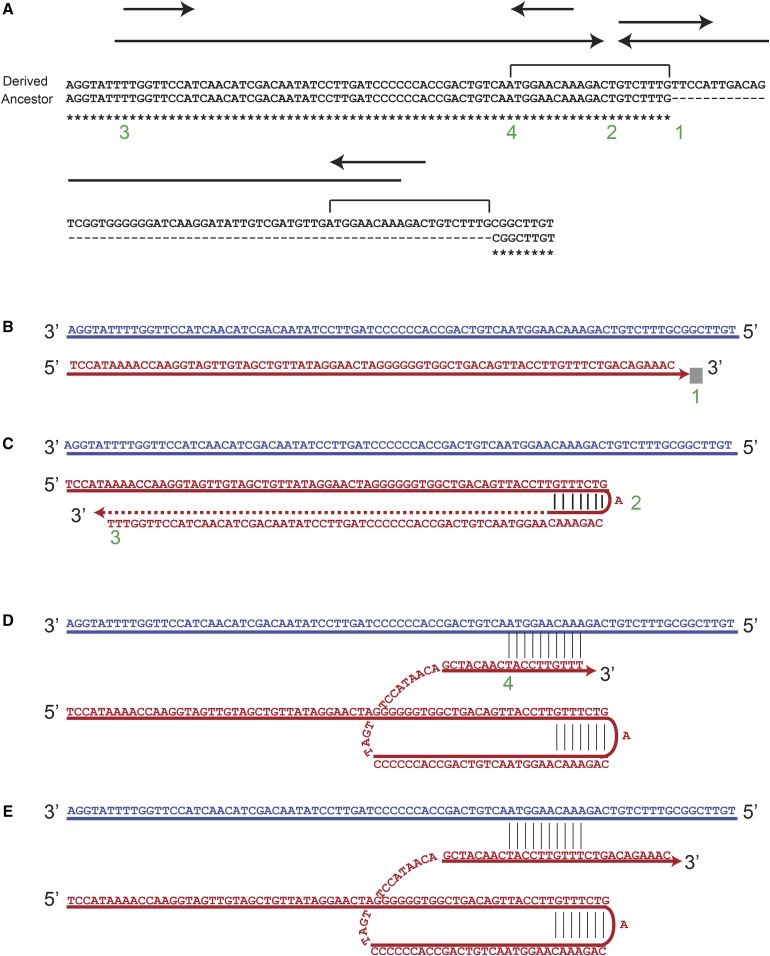
Figure 6.
Palindrome expansion occurs via template switching in rad27Δ strains. Insertion at ChrII 715496. (A) The top line includes the mutated strain with an insertion mediated by a palindrome; the bottom line is the original sequence. Arrows indicate palindromes, and brackets indicate duplications. Numbers indicate important points in the mechanism. (B) DNA synthesis starts on a template similar to the bottom line in A and continues until the fork is stalled (point 1). (C) At point 2, the DNA folds back (template switch #1) and synthesizes until it arrives at point 3. (D) The synthesized strand aligns back to the chromosome at point 4 (template switch #2) and (E) continues synthesis in the original direction. The top strand resembles the bottom and original strain in A, and the bottom strand resembles the top and mutated strain in A. The next round of replication results in two daughter cells with the rearrangements depicted in A. The red strand is the nascent strand and the blue strand is the original template strand.